100 VA Disability Rating: Understanding Maximum Compensation Pathways
A 100% VA disability rating represents the highest level of compensation available to veterans through the Department of Veterans Affairs. This comprehensive guide provides an overview of the pathways, evidence requirements, and considerations involved in VA evaluation for maximum compensation through either schedular rating or Total Disability Individual Unemployability (TDIU).
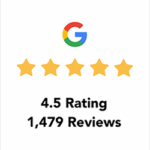
The VA evaluates disabilities against specific rating criteria outlined in their schedule, which details what symptoms and limitations qualify for each percentage level. The VA may award compensation at the 100% rate through two primary methods: accumulating individual disability ratings that combine to 100% (schedular rating), or demonstrating that service-connected disabilities prevent substantial gainful employment (TDIU). Each pathway involves different types of evidence and approaches.
Understanding these fundamentals helps veterans understand how the VA applies different evaluation methods to their situation. Some veterans have combined ratings that reach 100% schedularly toward 100%, while others find TDIU provides a more applicable route based on their circumstances.
TL;DR
- 100% VA disability rating represents the highest compensation level, achievable through either schedular rating or Total Disability Individual Unemployability (TDIU)
- TDIU allows payment at the 100% rate when VA criteria are met even with lower combined ratings when they cannot maintain gainful employment
- VA math does not work like regular addition—understanding their calculation method is important for rating considerations
- Medical evidence from multiple sources may be reviewed by the VA during evaluation
- The VA evaluates both schedular increases and TDIU based on specific evidence requirements
- 100% ratings come with maximum monthly compensation plus enhanced healthcare and dependent benefits
- Permanent and Total (P&T) designations provide additional protections and benefits beyond standard 100% ratings
- Independent medical evaluations can provide objective medical documentation for VA review
Understanding 100% VA Disability Rating Fundamentals
The 100 VA disability rating stands as the highest level of veteran disability compensation, representing complete disability or unemployability due to service-connected conditions. This rating requires meeting specific medical and functional criteria through comprehensive evaluation processes that examine both the severity of conditions and their impact on daily life and work capacity.
Two distinct paths lead to 100% compensation. Veterans can either accumulate individual disability ratings that combine to 100% (called schedular rating), or demonstrate that service-connected disabilities prevent them from maintaining substantially gainful employment through TDIU. Each path requires different types of evidence.
The VA’s definition of “total disability” does not necessarily mean complete incapacitation. Instead, it means service-connected conditions either meet the 100% criteria in their rating schedule or prevent working in a substantially gainful capacity. This distinction matters because it opens possibilities for veterans who might not initially think they qualify.
Veterans seeking to understand their options can learn more about requesting a VA disability rating increase as part of their research into pursuing higher compensation levels.
Total Disability Individual Unemployability (TDIU) Pathways
TDIU is a VA benefit that allows payment at the 100% rate under specific criteria when their service-connected conditions prevent substantial gainful employment, even if their combined disability rating falls below 100%. This benefit applies when the VA determines service-connected disabilities prevent substantially gainful employment that exceeds what their numerical ratings might suggest. TDIU comes in two forms: schedular TDIU with specific rating requirements, and extra-schedular TDIU for unique circumstances.
Schedular TDIU Requirements
Schedular TDIU follows specific rating thresholds that veterans must meet for consideration. According to VA regulations, veterans need either one disability rated at 60% or higher, or multiple disabilities where one rates at 40% or higher with a combined rating of 70% or more. These thresholds represent the VA’s assessment of disability levels that typically interfere with employment.
| TDIU Type | Rating Requirements | Additional Criteria |
| Schedular TDIU | One disability ≥60% OR Combined ≥70% with one ≥40% | Must demonstrate unemployability |
| Extra-schedular TDIU | Below schedular thresholds | Exceptional circumstances preventing employment |
| Temporary TDIU | Meets rating requirements | Temporary unemployability due to treatment |
Meeting these rating thresholds represents the initial consideration, but veterans must also demonstrate unemployability. The VA does not automatically grant TDIU based solely on meeting the rating requirements. Documentation must show how specific disabilities prevent maintaining substantially gainful employment.
The standard is “substantially gainful employment,” which the VA defines as work that provides income above the federal poverty threshold. Part-time work or jobs that accommodate disabilities may not automatically disqualify veterans from TDIU consideration.
Extra-schedular TDIU Considerations
Extra-schedular TDIU allows individual review under VA regulations for veterans whose unique circumstances demonstrate unemployability despite not meeting standard rating thresholds. This pathway requires individual consideration of how specific disability combinations or unusual manifestations affect employment. The VA evaluates these cases based on the totality of circumstances rather than rigid rating requirements.
Extra-schedular cases typically require more comprehensive evidence. Veterans are demonstrating that their specific situation creates unemployability that the standard rating criteria do not capture. This might involve unusual combinations of disabilities or conditions that manifest in ways not typical for their rating level.
Extra-schedular consideration requires documentation reviewed by the VA under regulatory standards of unemployability—showing how disabilities interact with each other and create barriers to employment that exceed what their individual ratings suggest.

Employment Documentation Process
The employment documentation process for TDIU requires comprehensive evidence demonstrating inability to maintain substantially gainful employment due to service-connected disabilities. This involves gathering detailed work history, medical evidence linking disabilities to employment limitations, and employer statements that corroborate functional restrictions.
Work history tells the story of how disabilities affected employment over time. The VA reviews patterns of job changes, reduced hours, or inability to perform essential job functions due to service-connected conditions.
Employment Documentation Checklist:
- Complete work history with dates and reasons for leaving positions
- Employer statements detailing disability-related work limitations
- Medical records linking conditions to work restrictions
- Evidence of accommodation attempts
- Documentation of job search efforts and barriers encountered
- Vocational expert opinions when applicable
Employer statements may be considered by the VA in TDIU cases. Former supervisors or HR representatives can provide objective perspectives on how disabilities affected work performance. These statements should focus on specific examples of how conditions interfered with job duties.
Medical evidence must connect disabilities to specific work limitations. Detailed explanations of how conditions prevent performing various types of work are more valuable than generic statements. Functional capacity evaluations provide objective clinical measurements of work-related limitations.
Combined Rating Calculations Explained
Achieving a 100% schedular rating requires understanding the VA’s approach to combining multiple disability ratings. Rather than simple addition, the VA uses a specific calculation method where each disability is applied against remaining efficiency. This system means that progressing from 90% to 100% often requires different considerations than accumulating lower-level ratings.
VA Math Methodology
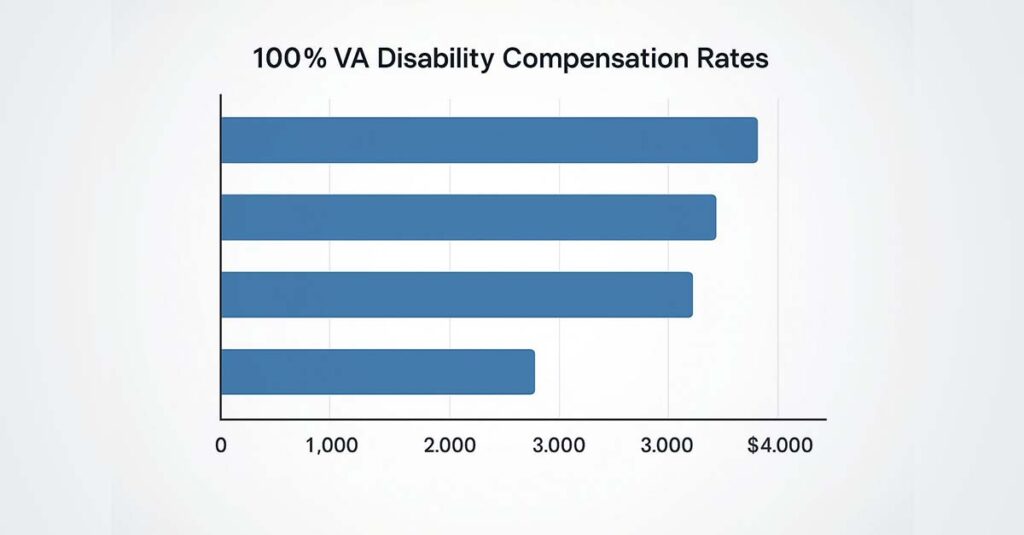
The VA’s formula for combining ratings operates on the principle that each disability affects remaining efficiency rather than adding to total disability percentage. This approach means that a veteran with multiple 50% disabilities does not automatically receive a 100% combined rating.
Here’s how it works: Start with the highest rating and subtract it from 100%. Apply the next highest rating to that remainder. For example, with ratings of 70% and 50%, there is 30% remaining efficiency after the first disability. The 50% disability affects that 30%, adding 15% to the total for a combined rating of 85%.
The VA rounds combined ratings to the nearest 10%, but only at the final calculation. Individual steps use precise percentages, which means small rating changes can sometimes affect important thresholds. A combined rating of 94.5% rounds to 100%, while 94.4% rounds to 90%.
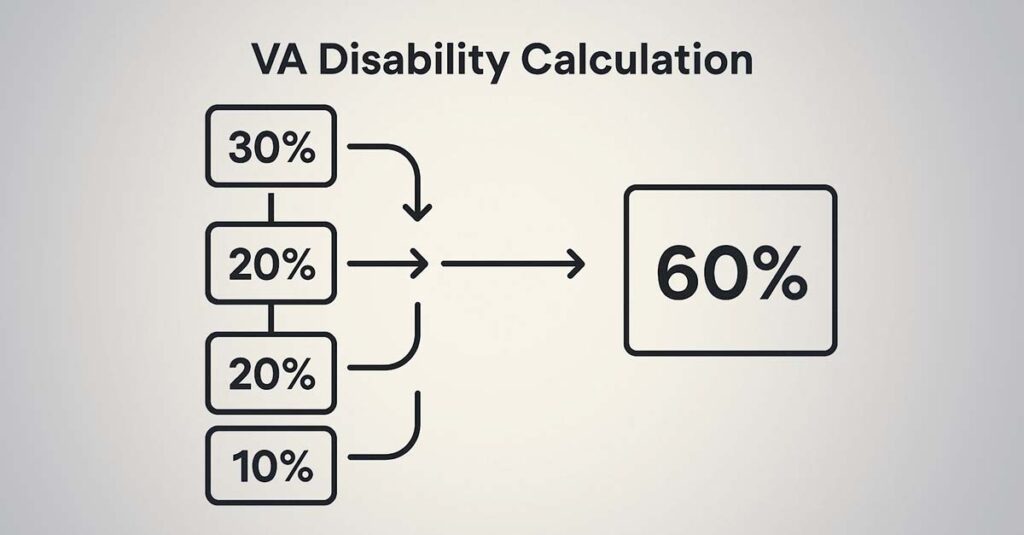
Example Calculation:
A veteran with PTSD (70%), degenerative disc disease (40%), and tinnitus (10%) would calculate as follows: Start with 70%, leaving 30% efficiency. Apply 40% to the remaining 30% (30% × 40% = 12%), adding 12% for a subtotal of 82%. Then apply 10% to the remaining 18% (18% × 10% = 1.8%), adding 1.8% for a final combined rating of 83.8%, which rounds to 80%.
This system makes understanding current ratings important when considering which conditions to pursue for evaluation. Different conditions may affect how the VA calculates combined ratings than focusing on existing ratings.
Understanding bilateral factor calculations adds another layer. When disabilities affect paired body parts (like both arms or legs), the VA applies an additional factor that can affect the combined rating.
| Current Combined Rating | Additional Rating Impact on Next 10% Threshold |
| 50% | 30% additional rating needed for 70% |
| 60% | 25% additional rating needed for 70% |
| 70% | 34% additional rating needed for 80% |
| 80% | 50% additional rating needed for 90% |
| 90% | 50% additional rating needed for 100% |

Medical Evidence Requirements
A 100% VA disability rating requires extensive medical documentation under VA criteria that demonstrates either complete disability according to VA rating schedules or total unemployability due to service-connected conditions. This evidence should come from multiple sources, including treating physicians, specialists, and comprehensive functional assessments that clearly show the severity and impact of conditions.
The VA evaluates ratings based on medical evidence in the record that supports claimed levels of impairment. This means detailed medical records, current examination findings, and professional opinions that align with the VA’s rating criteria.
Treating physicians play an important role because they observe conditions over time. Their treatment notes, progress reports, and opinions about functional limitations carry weight. However, these physicians benefit from understanding what the VA evaluates in disability assessments, which differs from regular medical treatment approaches.
Specialist evaluations become valuable for complex conditions or when disabilities affect multiple body systems. A rheumatologist’s opinion about joint conditions, combined with a psychiatrist’s assessment of mental health, creates a comprehensive picture.
Current medical evidence matters more than older records. The VA evaluates present levels of disability. Recent examinations, updated diagnostic tests, and current treatment records demonstrate ongoing disability status.
Functional capacity evaluations provide objective measurements of capabilities and limitations. These assessments test physical abilities, cognitive function, and work-related capabilities in controlled settings, offering concrete evidence beyond subjective symptom reports.
Medical Documentation Requirements
Medical documentation for 100% ratings includes current medical examinations, comprehensive treatment records, specialist opinions, and functional capacity evaluations that demonstrate the severity of conditions according to VA rating criteria. The documentation should establish not just the presence of disabilities, but their specific impact on daily functioning and work capacity.
Current medical examinations form the foundation of evidence. These exams should be recent (typically within the past year) and comprehensive enough to address all aspects of disabilities. Detailed evaluations that specifically address functional limitations caused by conditions are more valuable than generic check-ups.
Treatment records should show consistent medical care and document the progression or stability of conditions. Continuous treatment records provide context for current disability levels.
Medical Evidence Checklist:
- Recent comprehensive medical examinations (within 12 months)
- Continuous treatment records showing condition progression
- Current diagnostic test results (X-rays, MRIs, blood work)
- Specialist evaluations for complex conditions
- Functional capacity evaluation results
- Medical opinions linking conditions to functional limitations
- Medication lists and treatment response documentation
Diagnostic test results provide objective evidence of conditions. X-rays showing joint damage, MRIs revealing nerve compression, or psychological testing demonstrating cognitive impairment offer concrete documentation that supports disability claims.
Medical opinions need to address specific questions about functional limitations. Explanations of how conditions affect ability to work, perform daily activities, or function in various environments are more valuable than generic statements about having a condition.
Independent Medical Evaluations
Independent medical evaluations provide objective, third-party assessments that can complement VA examinations. These evaluations offer additional medical perspectives on condition severity and functional limitations, often providing more detailed analysis than standard VA compensation and pension exams.
Independent evaluations offer advantages because private physicians often have more time to conduct thorough evaluations and can focus specifically on aspects of conditions that matter for disability evaluation.
These evaluations work best when the examining physician understands VA disability criteria and rating schedules. Choosing someone with relevant experience may offer additional medical perspective.
Independent evaluations can address specific questions that VA exams might not fully explore. When VA examination documentation does not adequately assess certain aspects of a condition, independent evaluation can provide additional evidence.
REE Medical coordinates access to independent, licensed healthcare professionals who complete Disability Benefits Questionnaires (DBQs) and medical evaluations. Providers are familiar with disability-focused documentation and VA-standardized forms. For veterans pursuing 100% ratings, REE Medical coordinates independent medical documentation that may be reviewed by the VA for schedular ratings or TDIU consideration. Their experienced team works with providers familiar with VA-standardized documentation, coordinating independent medical documentation to support accurate evaluation of service-connected conditions.

Application Process and Timing Considerations
Successfully pursuing a 100% VA disability rating involves planning that considers whether to pursue individual disability increases toward a schedular 100% rating or apply for TDIU based on unemployability. The timing of applications, choice between initial claims versus increase claims, and coordination of evidence gathering are evaluated by the VA based on regulatory criteria.
Filing Considerations and Timing
Veterans make decisions about whether to pursue individual disability rating increases toward 100% schedular rating or apply for TDIU based on unemployability, as each approach requires different types of evidence and timing considerations. The choice depends on current ratings, medical evidence, employment history, and individual circumstances.
Choosing between pursuing schedular 100% or TDIU depends on current situation and available evidence. Veterans close to 100% through combined ratings with strong medical evidence for rating increases might focus on the schedular route. However, when disabilities clearly prevent employment but ratings seem difficult to increase, TDIU could be more applicable.
Current combined rating affects planning. Veterans with 70% or 80% combined ratings may meet TDIU consideration criteria than attempting to reach 100% schedular, depending on their employment situation. The evidence requirements for TDIU focus on unemployability rather than meeting specific rating criteria for individual conditions.
Example Consideration:
A veteran with a 70% combined rating from PTSD (50%), back injury (30%), and tinnitus (10%) might consider TDIU rather than focusing solely on increasing individual ratings. With documented employment difficulties due to PTSD symptoms and chronic pain, TDIU could provide a path to 100% compensation based on unemployability.
Employment status affects timing decisions. Veterans currently working but experiencing difficulties due to disabilities benefit from documenting those challenges. Veterans who have stopped working need evidence about how their disabilities prevent returning to employment.
Both approaches can be considered simultaneously or sequentially, depending on circumstances. Sometimes pursuing individual rating documentation first provides additional evidence that supports later TDIU consideration.
Initial vs. Increase Claims
The distinction between initial claims and increase claims affects both evidence requirements and approaches. New veterans typically file initial claims that establish service connection and initial ratings simultaneously, while veterans with existing service-connected disabilities file increase claims when conditions worsen.
Initial claims offer the opportunity to establish both service connection and ratings simultaneously. Veterans with severe conditions might achieve 100% ratings from their first claim with comprehensive medical evidence and proper documentation.
The advantage of initial claims lies in establishing baseline ratings without previous rating decisions to address. Veterans demonstrate current severity rather than arguing that conditions have worsened.
Increase claims require demonstrating that conditions have gotten worse since the last rating decision. This means evidence showing progression or worsening of symptoms, not just continued presence of the same condition at the same level.
The effective date rules differ between initial and increase claims, affecting when higher compensation begins. Understanding these rules from the Department of Veterans Affairs supports proper timing of applications.
Filing Preparation Template:
- Assessment Phase: Evaluate current ratings, medical evidence, and employment status
- Evidence Gathering: Collect recent medical records, employer statements, and functional assessments
- Approach Selection: Consider schedular increase, TDIU, or combined approaches
- Documentation Preparation: Complete appropriate forms and organize supporting evidence
- Submission and Follow-up: Submit claim and monitor progress through VA systems
Benefits and Long-term Management
A 100% VA disability rating provides maximum monthly compensation along with enhanced healthcare benefits, dependent coverage, and access to various state and federal programs. However, maintaining this rating requires understanding review processes, reporting requirements, and potential changes that could affect status over time.
Compensation and Additional Benefits
100% disabled veterans receive the highest monthly compensation rates that adjust annually for cost-of-living increases, plus additional allowances for dependents and special circumstances. Beyond monetary compensation, these veterans gain priority healthcare access, potential dependent healthcare coverage, and educational benefits that often extend to family members.
Monthly Compensation
The monthly compensation for 100% disabled veterans represents provides the highest VA disability compensation rate. These payments arrive monthly and adjust each December based on cost-of-living increases, providing some protection against inflation. Current rates are published by the Department of Veterans Affairs.
Additional compensation for dependents can increase monthly payments. Married veterans receive additional amounts for their spouse, with additional amounts for each child under 18 (or under 23 if in school). Dependent parents can also qualify for additional compensation under certain circumstances.
The tax-free nature of VA disability compensation makes it more valuable than equivalent taxable income. Veterans do not pay federal or state income taxes on disability payments, which is not subject to federal income tax.
Healthcare and Dependent Benefits
Veterans with 100% ratings receive priority healthcare access through the VA system, often including comprehensive medical, dental, and mental health services. The VA covers most medical expenses for 100% disabled veterans, including prescription medications, specialist care, and emergency treatment.
CHAMPVA provides healthcare coverage for dependents of 100% disabled veterans, offering an alternative to private health insurance. This coverage includes medical, surgical, and mental health services. More information is available from the VA CHAMPVA program.
Educational benefits for dependents can include tuition assistance, monthly housing allowances, and book stipends. The Fry Scholarship provides these benefits to survivors of veterans who died from service-connected conditions, while transferred GI Bill benefits allow veterans to share their education benefits with family members.
Maintaining 100% Status
Veterans should understand that 100% ratings may be subject to periodic reviews to assess whether conditions remain at the 100% level. This requires maintaining current medical evidence, continuing appropriate treatment, and understanding reporting requirements. However, certain protections exist for long-term 100% ratings and veterans over specific ages.
Periodic Reviews and Examinations
The VA may schedule periodic reviews for 100% ratings to determine if conditions remain at the same severity level, particularly for conditions considered likely to improve over time. These reviews require maintaining current medical documentation and continuing appropriate treatment to demonstrate ongoing disability.
Not all 100% ratings face the same review requirements. Static conditions that are unlikely to improve rarely receive reviews, while conditions that might improve over time may face more frequent examinations. Understanding which category conditions fall into supports appropriate preparation.
Maintaining regular medical care becomes important for rating reviews. Consistent medical records showing ongoing symptoms and limitations provide evidence that 100% rating remains appropriate.
Review Preparation Checklist:
- Maintain continuous medical treatment records
- Document ongoing symptoms and limitations
- Keep current diagnostic test results
- Update functional capacity assessments
- Prepare lay statements from family and friends
- Gather employer accommodation documentation
- Review VA rating criteria for your conditions
Age provides some protection against rating reductions. According to VA regulations, veterans over 55 receive additional protections, and those over 65 face fewer reviews. These age-based protections recognize that conditions are less likely to improve significantly in older veterans.
Special Circumstances and Exceptions
Certain unique situations provide alternative pathways to 100% compensation or equivalent benefits through special programs and designations. These include Permanent and Total (P&T) designations that offer additional protections, Special Monthly Compensation (SMC) for severe disabilities, and Combat-Related Special Compensation (CRSC) for military retirees.
Permanent and Total (P&T) Designations
Permanent and Total designations provide enhanced protections for veterans with 100% ratings whose conditions are unlikely to improve, offering additional benefits and safeguards against future rating reductions. These designations distinguish between static conditions that rarely change and non-static conditions that might be subject to periodic review.
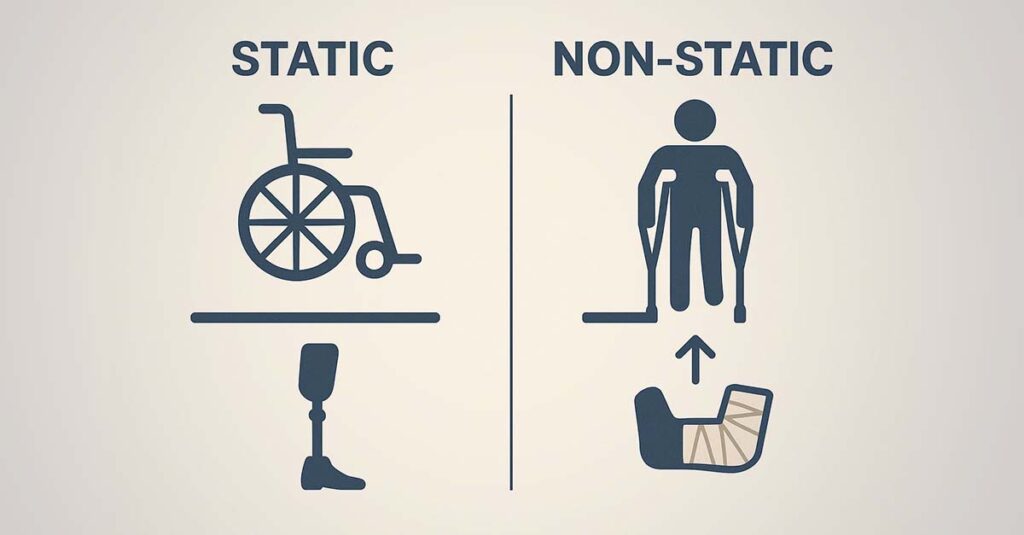
Static vs. Non-Static Conditions
Static conditions are those unlikely to improve over time and typically receive permanent protection from rating reductions. Non-static conditions may be subject to periodic reviews and potential rating changes. The distinction affects how often the VA schedules review examinations and what protections veterans receive.
Static conditions include things like amputations, certain spinal cord injuries, and severe traumatic brain injuries that are unlikely to improve significantly. These conditions rarely face review examinations because medical science does not expect meaningful recovery.
Non-static conditions might include mental health disorders, back injuries, or other conditions where improvement is possible with treatment. These conditions may face more frequent reviews, though the VA still provides some protections against rating reductions.
Protected Ratings Timeline
Veterans with continuous 100% ratings for specific time periods gain additional protections against rating reductions even if conditions show some improvement. These protections typically begin after 20 years of continuous 100% rating and provide significant safeguards for long-term disabled veterans.
Twenty-year continuous ratings receive substantial protection from reduction. Per VA regulations, the VA cannot reduce ratings below the level held for 20 years without clear and convincing evidence of sustained improvement.
Five-year continuous ratings also receive some protection, though not as extensive as the 20-year rule. The VA must provide clear evidence of sustained improvement before reducing ratings that have been stable for five years or more.
Special Monthly Compensation (SMC)
Special Monthly Compensation provides additional payments beyond the basic 100% rate for veterans with severe disabilities such as loss of limbs, blindness, or need for aid and attendance. SMC recognizes that some disabilities create extraordinary impacts that warrant compensation above the standard 100% level.
Aid and Attendance Benefits
Veterans requiring daily assistance with basic life functions may qualify for additional monthly compensation through Aid and Attendance benefits, which supplement regular disability payments. These benefits recognize the extra costs and limitations associated with needing help with activities like bathing, dressing, eating, or managing medications.
Aid and Attendance benefits apply when regular assistance with daily living activities is needed due to service-connected disabilities. This might include help with personal hygiene, meal preparation, medication management, or mobility assistance.
The additional compensation for Aid and Attendance can be substantial, often adding hundreds of dollars to monthly payments. This extra amount helps offset the costs of care assistance or acknowledges the burden placed on family members who provide care.
Example:
A veteran with severe PTSD, traumatic brain injury, and mobility issues who requires daily assistance with medication management, personal hygiene, and meal preparation could qualify for Aid and Attendance benefits, providing additional monthly compensation as determined by the VA.
Housebound Benefits
Veterans substantially confined to their homes due to disabilities may receive supplemental compensation beyond standard 100% rates through Housebound benefits. These benefits recognize that some disabilities create such severe limitations that veterans cannot leave their homes regularly for work, social activities, or routine errands.
Housebound benefits apply when disabilities substantially confine veterans to their home and immediate premises. This does not mean never leaving, but disabilities must severely limit ability to leave home for normal activities.
Combat-Related Special Compensation (CRSC)
Combat-Related Special Compensation allows military retirees to receive additional tax-free payments for combat-related disabilities while still collecting their retirement pay. CRSC serves as an alternative to concurrent receipt for retirees whose disabilities directly resulted from combat operations, training, or hazardous duty.
CRSC provides a way for military retirees to receive both retirement pay and disability compensation for combat-related conditions without the usual offset. Normally, disability compensation reduces retirement pay dollar-for-dollar, but CRSC allows receiving both.
The combat-related requirement means disabilities must have resulted directly from combat operations, combat training, or other hazardous military duties. More information is available from the Defense Finance and Accounting Service.

Common Challenges and Solutions
Veterans pursuing 100% ratings face specific obstacles including complex application processes, evidence requirements, and potential appeals when initial claims are denied. Understanding common challenges and their solutions supports more effective navigation of the system.
Appeals and Review Processes
When initial 100% rating requests are denied, veterans have multiple appeal options including supplemental claims with new evidence, higher-level reviews by senior raters, and Board of Veterans’ Appeals hearings. Each appeal pathway has different requirements, timelines, and advantages depending on specific circumstances.
Supplemental claims work best when new and relevant evidence exists that was not part of the original claim. This might include additional medical records, updated examinations, or new medical opinions that support the 100% rating request.
Higher-level reviews focus on whether the original decision-maker made errors in evaluating existing evidence. These reviews do not consider new evidence but can identify mistakes in how the VA applied their own regulations.
Board of Veterans’ Appeals hearings provide comprehensive review, allowing veterans to present their case directly to a Veterans Law Judge. These hearings can consider new evidence and provide opportunities to explain aspects of cases that might not be clear from written records.
Appeal Approach Considerations:
- Supplemental Claim: New medical evidence, additional diagnoses, updated examinations
- Higher-Level Review: Rating calculation errors, misapplied regulations, overlooked evidence
- Board Appeal: Complex cases requiring detailed explanation, witness testimony
The choice between appeal options depends on why the claim was denied and what additional evidence can be provided. Claims denied for lack of evidence might benefit from supplemental claims, while claims denied due to rating errors might work better with higher-level reviews.

Professional Support and Resources
Veterans benefit from professional guidance in navigating complex 100% rating requirements, evidence gathering, and appeal processes. This support can include accredited representatives, medical professionals who understand VA requirements, and organizations that specialize in veteran disability claims.
Accredited representatives understand VA regulations and procedures. They can assist with navigating complex requirements, avoiding common mistakes, and presenting cases effectively.
Medical professionals who understand VA disability evaluations can provide more effective evidence than those unfamiliar with the system. These professionals know what the VA evaluates and can tailor their evaluations and opinions accordingly.
Veterans Service Organizations (VSOs) provide free assistance to veterans pursuing disability claims. The quality and availability of assistance can vary between different organizations and individual representatives. A directory of accredited VSOs is available from the VA Office of General Counsel.
REE Medical coordinates access to independent, licensed healthcare professionals who complete Disability Benefits Questionnaires (DBQs) and medical evaluations. Providers are familiar with disability-focused documentation and VA-standardized forms. For veterans pursuing 100% ratings, REE Medical’s services provide medical evidence that can support both schedular 100% ratings and TDIU considerations. Their experienced team understands how disabilities align with VA Rating Schedules, coordinating the precise medical documentation needed to support accurate evaluation.
Professional Support Comparison:
- VSOs: Free service, variable quality, suitable for straightforward cases
- Private Attorneys: Fee-based, specialized expertise, beneficial for complex appeals
- Medical Professionals: Independent evaluations, objective evidence, valuable for comprehensive documentation
- Vocational Experts: Employment impact analysis, important for TDIU claims

Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between schedular 100% and TDIU?
According to the VA, schedular 100% rating is achieved when combined individual disability ratings mathematically equal 100% using VA calculation methods, or when a single condition meets the criteria for a 100% rating under the VA’s rating schedule. Per VA regulations, TDIU allows veterans to receive compensation at the 100% rate when their service-connected disabilities prevent them from maintaining substantially gainful employment, even if their combined rating is less than 100%.
What are the rating requirements for schedular TDIU?
Per VA regulations, schedular TDIU consideration requires either one disability rated at 60% or higher, or multiple disabilities where one rates at 40% or higher with a combined rating of 70% or more. According to the VA, meeting these thresholds allows for TDIU consideration, but veterans must still demonstrate that their service-connected conditions prevent substantially gainful employment.
How does the VA calculate combined disability ratings?
According to the VA, combined ratings are calculated using a specific methodology where each disability is applied against remaining efficiency rather than added together. Per VA math, a 70% rating leaves 30% efficiency, and a subsequent 50% rating affects that remaining 30%, adding 15% for a combined 85%. The VA rounds final combined ratings to the nearest 10%.
What is Permanent and Total (P&T) status?
Per VA policy, Permanent and Total status indicates that a veteran’s 100% disability rating is not expected to improve and is protected from routine review examinations. According to the VA, P&T status provides additional benefits including dependent educational assistance and stronger protections against rating reductions.
What additional benefits come with a 100% VA disability rating?
According to the VA, 100% disabled veterans receive maximum monthly compensation, priority VA healthcare access, potential CHAMPVA coverage for dependents, and various state benefits that vary by location. Per VA guidance, additional allowances are available for dependents, and Special Monthly Compensation may apply for veterans with specific severe disabilities.
Final Thoughts
Achieving a 100 VA disability rating represents the highest VA disability compensation level that can provide financial security and healthcare benefits for veterans and their families. Whether pursuing schedular 100% rating through combined individual ratings or TDIU based on unemployability, understanding the specific requirements and preparing comprehensive evidence are essential elements of the process.
The path to a 100% VA disability rating involves both understanding the system and meticulous preparation. Veterans who understand the distinction between schedular ratings and TDIU, comprehend the complexities of VA mathematics, and gather comprehensive medical evidence are better informed about the evaluation process.
Service-connected disabilities deserve recognition at their true severity level. Whether conditions meet the criteria for schedular 100% ratings or prevent maintaining gainful employment through TDIU, the evidence presented and the approach employed will influence the outcome.
100% ratings provide more than just maximum monthly compensation—they unlock priority healthcare, dependent benefits, educational opportunities, and long-term financial security. These comprehensive benefits are determined by VA eligibility and evaluation criteria in proper preparation and professional guidance when necessary.
The VA disability system continues evolving, with new recognition of conditions, updated rating criteria, and improved appeal processes. Staying informed about these changes and working with experienced professionals can make a difference in achieving appropriate compensation.
Initial setbacks should not discourage veterans from pursuing benefits earned through military service. Many veterans achieve 100% ratings through appeals, supplemental evidence, or alternative pathways after initial denials. VA decisions are based on evidence and regulatory standards.
Military service created the disabilities that now impact daily life and employment capacity. The VA’s 100% disability rating system exists to provide appropriate compensation for these service-connected conditions. With proper preparation, thoughtful approach, and comprehensive evidence, veterans can pursue the maximum benefits available for their unique circumstances.
Learn more about independent medical documentation and how the VA reviews medical evidence. Contact REE Medical for information about coordinating independent medical documentation.
Disclosure
DISCLAIMER: REE Medical, LLC is not a Veterans Service Organization (VSO) or a law firm and is not affiliated with the U.S. Veterans Administration (“VA”). Results are not guaranteed, and REE Medical, LLC makes no promises. REE Medical’s staff does not provide medical advice or legal advice, and REE Medical is not a law firm. Any information discussed, such as, but not limited to, the likely chance of an increase or service connection, estimated benefit amounts, and potential new ratings, is solely based on past client generalizations and not specific to any one patient. The doctor has the right to reject and/or refuse to complete a Veteran’s Disability Benefit Questionnaire if they feel the Veteran is not being truthful. The Veteran’s Administration is the only agency that can make a determination regarding whether or not a Veteran will receive an increase in their service-connected disabilities or make a decision on whether or not a disability will be considered service-connected. This business is not sponsored by, or affiliated with, the United States Department of Veterans Affairs, any State Department of Military and Veterans Affairs, or any other federally chartered veterans service organization.