VA Rating for Flat Feet: The Complete Guide to Understanding Your Disability Benefits
Flat feet may seem like a minor issue on the surface, but for many veterans, it represents a daily source of pain, instability, and functional limitations that can significantly impact work, mobility, and overall quality of life. Understanding how the VA evaluates pes planus, what evidence the VA reviews, and how ratings are assigned provides valuable insight into the disability compensation process.
Table of Contents
- Understanding Flat Feet as a VA Disability
- The Claims Process for Flat Feet Disability
- Medical Evaluation and Evidence Development
- Advanced Considerations for Flat Feet Claims
TL;DR
- Flat feet (pes planus) can qualify for VA disability ratings from 0% to 50% based on severity and functional limitations
- Service connection requires demonstrating the condition began during service, was aggravated by service, or developed secondary to another service-connected condition
- Comprehensive medical documentation focusing on functional limitations is central to accurate ratings
- Secondary conditions like plantar fasciitis, knee pain, and back problems often develop from flat feet and may warrant separate ratings
- Bilateral flat feet (affecting both feet) can increase overall compensation through the bilateral factor
- Independent medical evaluations provide thorough documentation that addresses VA rating criteria
- Complete evidence packages submitted at optimal times reduce processing delays and improve outcomes
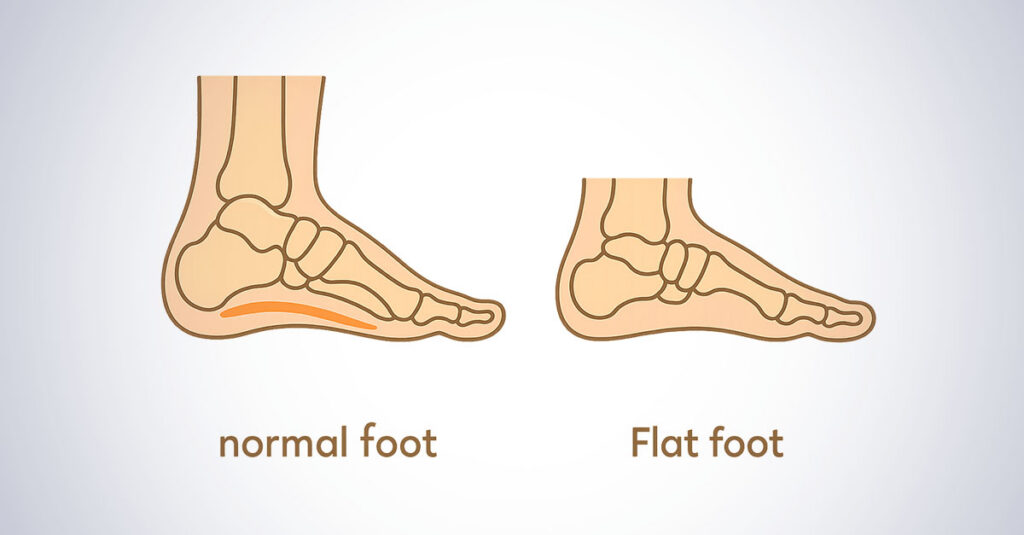
Understanding Flat Feet as a VA Disability
Flat feet represents more than just a structural foot abnormality—it’s a legitimate medical condition that can significantly impact daily life and qualify for VA disability compensation. This section explores the medical foundation of pes planus, how the VA evaluates this condition, and what veterans need to know about establishing service connection.
Veterans pursuing a flat feet claim benefit from understanding how VA disability ratings work to establish realistic expectations for compensation levels.
The Medical Foundation Behind Flat Feet
Understanding the clinical aspects of flat feet becomes important when seeking VA compensation, since the condition’s severity directly correlates to potential disability ratings. The anatomical changes that occur with pes planus extend beyond what appears on the surface.
What Actually Happens When Arches Collapse
The structural changes in flat feet affect the entire body’s biomechanics and create a cascade of compensatory issues that can impact quality of life and work capacity.
The foot’s arch serves as a natural shock absorber and weight distributor. When it collapses, the entire sole makes contact (or near-complete contact) with the ground. This fundamental change alters how forces travel through the body during walking, running, and standing.
The ripple effects extend far beyond the feet. Ankles, knees, hips, and even the lower back must compensate for the altered mechanics. This compensation pattern often leads to additional problems that may also qualify for VA ratings.
Primary vs. Secondary Flat Feet: Why the Distinction Matters
The origin of flat feet conditions affects how the VA evaluates service connection. As primary and secondary pes planus require different approaches to establishing service connection and may have varying implications for overall disability ratings.
Primary flat feet develops on its own, often due to genetic factors or natural aging processes. However, secondary flat feet—which is more common among veterans—results from trauma, overuse, or degenerative changes directly related to military activities.
Military service creates numerous scenarios that can trigger secondary pes planus. Heavy pack marching, prolonged standing on hard surfaces, jump training, and combat injuries all contribute to arch collapse. The distinction matters because secondary conditions often have clearer service connection pathways.
Establishing Service Connection
Service connection forms the foundation of VA disability claims, requiring clear links between military service and flat feet conditions. Three primary pathways exist for establishing this connection, each with specific evidence requirements.
Direct Service Connection: The Straightforward Path
Direct service connection offers the most straightforward route to VA compensation when evidence demonstrates that flat feet conditions either began during service or resulted from specific military incidents, though it requires the strongest documentation of service-related origin.
Evidence might include documentation of:
- Foot injuries during training or deployment
- Medical records showing arch problems that developed during service
- Incident reports from accidents that affected feet
- Progressive worsening documented in service medical records
Establishing clear timelines is important. Medical records from the service period and immediately after discharge become valuable evidence. Even brief mentions of foot pain or arch problems in service records can support claims.
When Pre-existing Conditions Get Worse
Veterans with flat feet that existed before military service can still qualify for VA compensation by demonstrating that service permanently worsened the condition beyond its natural progression, requiring specific documentation strategies to prove aggravation.
The VA recognizes aggravation of pre-existing conditions as valid grounds for service connection when evidence demonstrates that military service permanently worsened conditions beyond what would have occurred naturally.
Documentation becomes critical in these cases. Pre-enlistment medical records, service medical records showing progression, and post-service treatment records all contribute to building the case.
Secondary Service Connection: The Domino Effect
Secondary service connection acknowledges that flat feet can develop as a consequence of other service-connected conditions, creating opportunities for veterans whose pes planus resulted from compensatory changes due to existing disabilities.
Flat feet might develop because of another service-connected condition. This secondary connection pathway recognizes that injuries create compensatory patterns throughout the body.
Common scenarios include:
- Leg injuries that alter gait and stress arches
- Ankle injuries that change how weight distributes across feet
- Knee problems that force different walking patterns
- Hip conditions that affect entire lower extremity mechanics
Medical evidence must clearly show the connection between primary service-connected conditions and the development of flat feet. Independent medical opinions often provide strong support for these claims.
How the VA Rates Flat Feet
The VA uses diagnostic code 5276 to rate flat feet conditions, with ratings ranging from 0% to 50% based on severity of symptoms and functional limitations. Understanding these rating criteria helps clarify evidence requirements and set realistic expectations for claim outcomes.
| VA Rating | Symptoms | Foot Involvement | Key Characteristics |
| 0% | Mild symptoms completely relieved by arch supports/orthotics | One or both feet | Occasional pain, manageable with supportive footwear |
| 10% | Pain with manipulation/use, inward bowing of Achilles tendon | One or both feet | Weight-bearing line falls to medial edge, manageable symptoms |
| 20% | Marked deformity, pain with movement, swelling, callosities | One foot | Severe symptoms in single foot with visible deformity |
| 30% | Marked deformity, excessive pain and swelling OR pronounced symptoms | Both feet OR one foot | Bilateral moderate symptoms OR unilateral severe symptoms |
| 50% | Extreme pronation, marked tenderness, Achilles displacement | Both feet (bilateral) | Most severe rating requiring bilateral involvement |
The 0% Rating: Establishing Foundation
A 0% rating might not provide immediate compensation, but it establishes service connection that protects future interests and creates pathways for increases as conditions potentially worsen over time.
While a 0% rating doesn’t provide monthly compensation, understanding what a zero percent disability rating provides reveals important benefits including future protection and medical care access.
A 0% rating applies when flat feet are present but don’t cause significant functional impairment or pain. Occasional discomfort may occur, but it doesn’t substantially limit activities or work capacity.
10% Rating: When Symptoms Start Affecting Daily Life
The 10% rating threshold recognizes mild but noticeable symptoms that begin to impact daily activities, requiring documentation of occasional pain, slight swelling, or minor limitations in prolonged weight-bearing activities.
At the 10% level, flat feet cause mild but noticeable symptoms. Veterans might experience:
- Occasional pain during or after prolonged standing
- Slight swelling at the end of long days
- Minor limitations in walking long distances
- Discomfort that affects footwear choices or activities
Documentation showing how these symptoms, while mild, still impact daily life and work capacity becomes important for this rating level.
20% Rating: Moderate Impact on Daily Activities
A 20% rating reflects moderate symptoms that create clear limitations in occupational and recreational activities, requiring evidence of regular pain, noticeable swelling, and documented functional restrictions.
Symptoms become more consistent and limiting at this level. Regular pain, noticeable swelling, and clear activity limitations characterize a 20% rating.
Veterans might find themselves avoiding certain activities, needing frequent breaks during standing or walking, or experiencing pain that interferes with work tasks. The functional limitations become apparent and affect job performance or recreational choices.
30% Rating: Marked Symptoms with Significant Limitations
The 30% rating level acknowledges marked symptoms that substantially limit weight-bearing activities, requiring comprehensive documentation of significant pain, frequent swelling, and clear restrictions in ability to perform essential daily functions.
Marked symptoms define the 30% rating level. Flat feet cause significant pain, frequent swelling, and substantial limitations in weight-bearing activities.
At this level, conditions noticeably impact work capacity and daily functioning. Veterans might need work accommodations, experience difficulty with prolonged standing or walking, and find that symptoms affect sleep or overall quality of life.
50% Rating: Maximum Compensation for Severe Impact
The maximum 50% rating applies to the most severe flat feet cases, where constant pain, persistent swelling, and marked limitation of motion significantly impact daily functioning and may prevent normal work activities.
The maximum 50% rating applies when flat feet result in severe, constant symptoms that markedly limit daily functioning. Constant pain, persistent swelling, and significant motion limitations characterize this rating level.
Veterans at this level often cannot perform many routine activities without significant difficulty. Work capacity may be severely limited, and the condition substantially impacts overall quality of life.

The Claims Process for Flat Feet Disability
Successfully navigating the VA claims process for flat feet requires strategic preparation, comprehensive documentation, and understanding of evaluation timelines. Different claim types require different documentation approaches—initial claims for unrated conditions versus increase claims for worsening symptoms.
Building Initial Claim Strategy
First-time claimants must establish both the medical reality of their flat feet condition and its connection to military service, requiring strategic approaches to documentation gathering and evidence presentation that address VA evaluation criteria from the outset.
Essential Documentation: Claim Foundations
The strength of flat feet claims depends heavily on comprehensive documentation that clearly establishes the condition’s existence, severity, and service connection, requiring coordination of multiple evidence sources to build compelling cases.
Documentation packages form the backbone of entire claims. Without proper evidence, even legitimate conditions may receive denials or inadequate ratings.
Service medical records matter—every mention of foot pain, arch problems, or related issues is important. Post-service treatment records show the condition’s progression and current impact. Civilian medical records that document ongoing symptoms and treatment shouldn’t be overlooked.
Diagnostic imaging provides objective evidence of structural changes. X-rays can show arch collapse, while MRI or CT scans reveal soft tissue involvement and complications.
Personal statements detailing how flat feet affect daily activities, work capacity, and quality of life add context that medical records alone might miss.
Understanding the importance of medical evidence in VA disability claims clarifies why comprehensive documentation matters for successful flat feet cases.
Flat Feet Claim Documentation Checklist:
- ☐ Complete service medical records (request from NPRC if needed)
- ☐ All post-service medical records related to foot problems
- ☐ Current diagnostic imaging (X-rays, MRI, CT scans)
- ☐ Completed DBQ from qualified medical provider
- ☐ Personal statement describing symptom impact on daily life
- ☐ Lay statements from family/friends witnessing limitations
- ☐ Employment records showing work limitations or accommodations
- ☐ Medical opinion linking condition to service (if needed)
- ☐ Evidence of secondary conditions related to flat feet
Meeting Medical Evidence Standards
The VA requires current, comprehensive medical evidence that documents flat feet diagnosis, severity, and functional impact, with independent medical examinations often providing the most thorough documentation needed for accurate rating decisions.
The VA reviews current medical evidence showing diagnosis, severity, and functional impact. Routine doctor visits rarely provide the comprehensive evaluation needed for accurate ratings.
Independent medical examinations often exceed the quality of routine clinical appointments. These evaluations focus specifically on documenting all aspects relevant to VA rating criteria, including functional limitations that might be overlooked in standard medical care.
Medical evidence must address the specific criteria used in VA ratings. Generic statements about “foot pain” provide limited value—detailed documentation of arch collapse, weight-bearing limitations, and functional restrictions is necessary.
Consider a veteran whose medical records specifically document “bilateral pes planus with marked pronation causing pain during prolonged standing exceeding 30 minutes, requiring frequent position changes and limiting work capacity in retail environment” rather than simply stating “patient complains of foot pain.” The detailed functional documentation provides clearer evidence for rating decisions.
Pursuing Increases for Worsened Conditions
Veterans with existing flat feet ratings may qualify for increases when their conditions deteriorate, but success requires demonstrating clear progression of symptoms and increased functional limitations since their last evaluation, with strategic timing playing an important role.
Proving Condition Worsening
Increase claims require compelling evidence showing that flat feet conditions have deteriorated since last VA evaluations, necessitating documentation of worsening symptoms, increased functional limitations, or new complications that justify higher ratings.
Flat feet conditions might worsen over time due to aging, additional injuries, or progressive degeneration. Increase claims allow veterans to seek higher ratings when conditions deteriorate.
Evidence showing clear progression since last VA evaluations is necessary. This might include:
- New or worsening symptoms documented in medical records
- Increased functional limitations affecting work or daily activities
- Development of secondary conditions related to flat feet
- Changes in treatment requirements or medication needs
Evidence must show that conditions have permanently worsened, not just temporary flare-ups or seasonal variations.
Strategic Timing Considerations
The timing of increase claims significantly impacts effective dates for higher compensation, making it important to file promptly when significant changes in conditions occur rather than waiting for annual evaluations or routine appointments.
Veterans considering increases benefit from understanding how to request a VA disability rating increase effectively to maximize chances of approval and proper effective dates.
Timing increase claims strategically can affect compensation significantly. VA ratings typically become effective from the date claims are filed, not when symptoms actually worsened.
Filing increase claims as soon as significant, lasting changes in conditions occur is advisable. Delays can result in months of foregone higher compensation.
Documenting progression carefully matters. Keeping records of when symptoms worsened, how they affect daily activities, and any changes in treatment needs supports claims and helps establish effective dates.
Maximizing Combined Ratings and Secondary Conditions
Flat feet often contributes to or occurs alongside other musculoskeletal conditions, creating opportunities to increase overall disability compensation through combined ratings and secondary condition claims that recognize the interconnected nature of disabilities.
Common Secondary Conditions: The Ripple Effect
Veterans with flat feet frequently develop additional conditions due to altered biomechanics and compensatory movement patterns, with plantar fasciitis, ankle problems, knee pain, hip issues, and lower back problems representing common secondary conditions that may warrant separate ratings.
Flat feet rarely exists in isolation. The altered biomechanics create compensatory patterns that often lead to additional problems throughout the kinetic chain.
Plantar fasciitis frequently develops alongside flat feet as the collapsed arch stresses the plantar fascia. While related, these conditions can potentially receive separate ratings if each contributes distinct functional limitations.
Ankle problems often emerge as foot mechanics change. The altered weight distribution and motion patterns stress ankle joints and supporting structures.
Knee pain develops as the body compensates for the changed foot mechanics. The altered gait pattern and weight distribution affect knee alignment and loading patterns.
Hip and lower back problems can result from the compensatory changes that travel up the kinetic chain. These conditions might qualify for separate ratings if properly documented.
Understanding Bilateral Factor Benefits
When flat feet affects both feet, the VA applies a bilateral factor that provides additional compensation beyond standard rating calculations, recognizing that bilateral conditions create compounded disability impacts that exceed the sum of individual ratings.
Bilateral conditions receive special consideration in VA ratings. When flat feet affects both feet, veterans may qualify for the bilateral factor—additional compensation that recognizes the compounded impact of bilateral disabilities.
The bilateral factor doesn’t simply double ratings. Instead, it applies a complex calculation that provides additional compensation beyond what would be received for two separate unilateral conditions.
Even if flat feet affects both feet differently, bilateral consideration might still apply. The severity doesn’t need to be identical—the key is that both feet are affected by the service-connected condition.
Medical Evaluation and Evidence Development
Obtaining proper medical evaluation and developing strong evidence forms the cornerstone of successful flat feet disability claims. Comprehensive examination requirements, diagnostic testing protocols, and the critical role of Disability Benefit Questionnaires in documenting the condition’s full impact on daily functioning all contribute to accurate rating determinations.
Comprehensive Medical Examinations: Beyond Basic Checkups
Thorough medical evaluations provide the foundation for successful flat feet disability claims by documenting all aspects of conditions, requiring examinations that go far beyond routine clinical appointments to capture the full scope of functional limitations and biomechanical impacts.
Physical Examination Components That Matter
Complete flat feet examinations must include both weight-bearing and non-weight-bearing assessments, range of motion testing, strength evaluation, and gait analysis to fully characterize how conditions impact daily functioning and work capacity.
Examinations need to capture every aspect of how flat feet affects functioning. Standard medical appointments often miss details that drive VA rating decisions.
Weight-bearing and non-weight-bearing assessments reveal different aspects of conditions. Arch collapse might be more apparent under load, while non-weight-bearing examination shows the foot’s flexibility and structural changes.
Range of motion testing documents limitations in foot and ankle movement that contribute to functional restrictions. These measurements provide objective data supporting rating levels.
Strength evaluation identifies weakness in supporting muscles that might develop from altered mechanics or compensatory patterns. Muscle weakness can significantly impact functional capacity.
Gait analysis reveals how flat feet affects walking patterns and identifies compensatory changes that might lead to secondary conditions. These observations support both primary claims and potential secondary conditions.
Diagnostic Testing: Seeing Beyond the Surface
Appropriate diagnostic imaging including X-rays, CT scans, or MRI studies may be necessary to document structural abnormalities, rule out other conditions, and provide objective evidence of the severity of flat feet conditions.
Diagnostic imaging provides objective evidence that supports subjective symptoms. Different imaging modalities reveal various aspects of conditions.
X-rays show bone structure and alignment, revealing the degree of arch collapse and any associated bone changes. Weight-bearing X-rays are particularly valuable as they show feet under load.
CT scans provide detailed bone imaging and can reveal subtle fractures or bone changes that might not appear on standard X-rays. They’re particularly useful when complex structural abnormalities are suspected.
MRI studies show soft tissue involvement, including ligament damage, tendon problems, and inflammation that contribute to symptoms. This imaging can reveal complications that significantly impact functional capacity.
Obtaining imaging that specifically addresses VA rating criteria is important. Generic radiology reports might miss details needed for disability evaluation.
Functional Assessment Documentation: Where Ratings Are Determined
Evaluations must thoroughly document how flat feet affects ability to stand, walk, work, and perform daily activities, as these functional limitations directly drive VA rating decisions and determine compensation levels.
Functional limitations drive VA ratings more than structural abnormalities alone. Evaluations must clearly document how flat feet restricts daily activities and work capacity.
Standing tolerance becomes important documentation. How long can veterans stand before experiencing significant pain or fatigue? Do they need to shift weight frequently or take breaks?
Walking limitations affect both distance and terrain tolerance. Can veterans walk on uneven surfaces? How far can they walk before symptoms force rest?
Work capacity restrictions might include limitations in prolonged standing, walking on hard surfaces, or carrying heavy loads. These restrictions directly impact employability and earning capacity.
Daily activity limitations encompass everything from household chores to recreational activities. Documenting how flat feet affects ability to shop, clean, exercise, or participate in family activities provides important context.
Disability Benefit Questionnaire (DBQ) Completion
The DBQ for foot conditions provides a standardized format for documenting flat feet disabilities and ensuring all relevant information reaches VA decision-makers, but success depends on proper completion by qualified providers who understand VA rating criteria.
Veterans benefit from understanding the VA DBQ process to ensure their foot condition evaluation meets all requirements for accurate rating determination.
Critical DBQ Elements That Determine Ratings
Properly completed DBQs must comprehensively address the degree of arch collapse, presence of pain and swelling, functional limitations, and any secondary conditions related to flat feet, with each element directly influencing final rating determinations.
The DBQ serves as the primary communication tool with VA rating specialists. Every section matters, and incomplete or vague responses can result in lower ratings or claim denials.
Arch collapse documentation must be specific and measurable. Vague descriptions like “some flattening” don’t provide adequate information for accurate ratings. The DBQ should specify the degree of collapse and whether it’s flexible or rigid.
Pain and swelling descriptions need to address frequency, severity, and triggers. Constant pain receives different consideration than occasional discomfort. Swelling patterns and their relationship to activity levels provide rating information.
Functional limitation documentation drives rating levels. The DBQ must clearly describe specific activities that are limited, the degree of limitation, and how these restrictions impact daily life and work capacity.
Secondary condition identification helps maximize overall compensation. The DBQ should address any related conditions that might qualify for separate ratings.
Provider Qualifications: Why Expertise Matters
DBQs should be completed by qualified medical professionals familiar with VA rating criteria and experienced in conducting disability evaluations for veterans, as provider expertise significantly impacts the quality and completeness of documentation.
Not all medical providers understand VA rating criteria or disability evaluation principles. The provider completing DBQs can significantly impact claim success.
Qualified providers understand the specific language and documentation standards that VA rating specialists expect. They know which details matter most and how to present information effectively.
Experience with veteran disability evaluations helps providers recognize the functional limitations and secondary conditions commonly associated with flat feet. This experience translates into more comprehensive and accurate documentation.
Provider familiarity with VA regulations ensures that DBQs address all relevant rating criteria and avoid common pitfalls that can delay or derail claims.
A qualified provider completing a flat feet DBQ would document “bilateral pes planus with complete arch collapse, unable to perform single-limb heel rise test, experiences sharp pain after 15 minutes of standing requiring seated rest, uses custom orthotics with minimal symptom relief” versus a generic note stating “patient has flat feet and foot pain.”

Advanced Considerations for Flat Feet Claims
Complex scenarios and special circumstances in flat feet disability claims require nuanced understanding of VA regulations and rating methodologies. Bilateral versus unilateral rating strategies, the intricate relationship between flat feet and plantar fasciitis, and advanced techniques for maximizing overall disability compensation through strategic claim development all require careful consideration.
Bilateral vs. Unilateral Rating Strategies
The distinction between single-foot and both-feet involvement significantly impacts compensation calculations and rating approaches, with bilateral conditions receiving special consideration that can substantially increase overall disability compensation beyond simple mathematical addition.
Bilateral Factor Calculations: More Than Simple Math
When both feet are affected by flat feet, the VA applies a bilateral factor that increases combined ratings beyond simple addition, recognizing that bilateral conditions create compounded disability impacts that exceed what would be experienced with two separate unilateral conditions.
Bilateral flat feet receives special treatment in VA calculations that can significantly boost compensation. The bilateral factor recognizes that having both feet affected creates greater disability than the sum of two separate conditions.
The calculation isn’t straightforward doubling. Instead, the VA uses a complex formula that provides additional compensation beyond what would be received for two unilateral conditions rated separately.
For example, if each foot rates 20%, the combined rating doesn’t simply equal 40%. The bilateral factor calculation might result in a combined rating of 36% or higher, depending on other service-connected conditions.
This additional compensation acknowledges that bilateral conditions create unique challenges. When both feet are affected, compensating by favoring one side isn’t possible, leading to greater overall functional limitation.
| Bilateral Rating Scenario | Individual Foot Ratings | Standard Combined Rating | With Bilateral Factor | Monthly Compensation Difference |
| Mild Bilateral | 10% + 10% | 19% | 21% | ~$50 additional monthly |
| Moderate Bilateral | 20% + 20% | 36% | 40% | ~$200 additional monthly |
| Severe Bilateral | 30% + 30% | 51% | 56% | ~$300 additional monthly |
| Mixed Severity | 20% + 30% | 44% | 48% | ~$250 additional monthly |
| Maximum Bilateral | 50% (both feet) | 50% | 50% | No additional benefit |
Asymmetric Severity: When One Side Is Worse
Veterans may have different severity levels between their feet, requiring separate ratings for each foot before applying bilateral factors, with documentation strategies that clearly establish the distinct functional impacts of each foot’s condition.
Flat feet might affect each foot differently, requiring individual evaluation and rating for each side. This asymmetric presentation is common and can actually benefit overall ratings.
Each foot receives its own rating based on its individual severity and functional impact. The VA then combines these ratings using the bilateral factor to determine overall compensation.
Documentation must clearly distinguish between the conditions affecting each foot. Medical evaluations should address each foot separately, noting differences in arch collapse, pain levels, functional limitations, and treatment responses.
Asymmetric conditions often result in higher combined ratings than symmetric bilateral conditions. The variation in severity between sides can push combined ratings into higher compensation brackets.
Unilateral Compensation Strategies: Making the Most of Single-Foot Claims
Single-foot flat feet cases require focused strategies that demonstrate how the condition affects overall mobility and creates compensatory problems in other body parts, potentially leading to secondary condition claims that increase overall compensation.
Unilateral flat feet claims require different strategic approaches that emphasize the condition’s impact on overall functioning and mobility patterns.
Focus on demonstrating how single-foot flat feet affects the entire kinetic chain. The altered mechanics don’t stay isolated to one foot—they create compensatory changes throughout the body.
Documenting secondary conditions that develop from compensating for the affected foot becomes important. The opposite foot, ankle, knee, hip, and back often develop problems as they work harder to compensate for the flat foot.
Emphasizing functional limitations that result from having one “good” foot and one problematic foot matters. This imbalance can be more limiting than bilateral conditions in some activities.
Considering the long-term implications of unilateral flat feet is important. The compensatory patterns often lead to accelerated wear and problems in other body parts, supporting secondary condition claims.
Navigating Flat Feet with Plantar Fasciitis Combinations
The frequent co-occurrence of flat feet and plantar fasciitis creates complex rating scenarios that require careful evaluation of overlapping symptoms, with potential for separate ratings when each condition contributes distinct functional limitations beyond the other’s impact.
Justifying Separate Ratings: Avoiding the Pyramiding Trap
Veterans can potentially receive separate ratings for both flat feet and plantar fasciitis when each contributes distinct functional limitations beyond the other’s impact, but success requires careful documentation that clearly delineates each condition’s unique contributions to overall disability.
Flat feet and plantar fasciitis commonly occur together, creating complex rating scenarios that require careful navigation of VA regulations. The key challenge is avoiding pyramiding while maximizing compensation.
Pyramiding occurs when the VA rates the same symptoms under multiple diagnostic codes. VA regulations prevent this double-counting, but separate ratings are possible when conditions contribute distinct functional limitations.
For separate ratings, evidence must demonstrate that each condition creates unique functional restrictions beyond what the other condition produces. This requires detailed medical documentation that clearly distinguishes each condition’s individual impact.
Flat feet might limit ability to walk on uneven surfaces or stand for extended periods due to arch collapse and instability. Plantar fasciitis might create sharp, stabbing pain that’s worst in the morning or after periods of rest.
The functional limitations must be clearly different and additive. If both conditions simply cause “foot pain that limits walking,” pyramiding becomes likely. But if flat feet causes instability issues while plantar fasciitis causes specific pain patterns, separate ratings become possible.
Documenting Combined Functional Impact
Medical evidence must clearly demonstrate how flat feet and plantar fasciitis together create greater functional limitations than either condition would produce independently, requiring sophisticated documentation strategies that capture the synergistic effects of both conditions.
When both conditions are present, their combined impact often exceeds what either would produce alone. This synergistic effect can justify higher ratings or separate ratings for each condition.
Documenting how the conditions interact to worsen overall functional capacity becomes important. Flat feet might make plantar fasciitis worse by altering foot mechanics, while plantar fasciitis pain might force different walking patterns, worsening flat feet.
Treatment complications arise when both conditions are present. Interventions that help one condition might worsen the other, limiting treatment options and prolonging disability.
Activity restrictions become more complex with both conditions present. Veterans might avoid certain activities due to flat feet instability while also avoiding others due to plantar fasciitis pain, creating broader functional limitations than either condition alone would produce.
The combined conditions often require more complex treatment approaches, including specialized footwear, multiple types of therapy, and careful activity modification that goes beyond what either condition would require individually.
A veteran with both flat feet and plantar fasciitis might have documentation stating: “Bilateral pes planus causes instability requiring wide-based gait and avoiding uneven terrain, while plantar fasciitis creates severe morning pain requiring 10-15 minutes of stretching before weight-bearing and sharp pain with initial steps after prolonged sitting, together preventing standing work exceeding 2 hours and requiring multiple daily rest periods.” This documentation clearly distinguishes each condition’s unique functional impacts.
Flat Feet Secondary Conditions Tracking Template:
Primary Condition: Bilateral Pes Planus – Current Rating: ____%
Secondary Conditions to Monitor:
- ☐ Plantar Fasciitis (left/right/bilateral)
- ☐ Ankle Instability or Sprains
- ☐ Knee Pain (patellofemoral syndrome/osteoarthritis)
- ☐ Hip Pain (trochanteric bursitis/osteoarthritis)
- ☐ Lower Back Pain
- ☐ Achilles Tendonitis
- ☐ Shin Splints
- ☐ Bunions or Hammertoes
- ☐ Degenerative Joint Disease
Documentation Requirements for Each:
- Medical diagnosis with onset date
- Medical opinion linking to flat feet
- Functional limitations specific to each condition
- Treatment records and response
- Impact on daily activities and work capacity

How REE Medical Supports Veterans with Flat Feet Documentation
REE Medical coordinates independent medical evaluations that provide veterans with comprehensive, VA-compliant documentation for flat feet claims. Through a nationwide network of licensed medical professionals who specialize in disability-focused documentation, REE Medical connects veterans with qualified physicians who understand the specific requirements for flat feet DBQs.
The coordination process begins with a complimentary consultation to explain how independent medical documentation is developed. REE Medical’s staff coordinates access to licensed healthcare professionals familiar with VA-standardized forms and disability-focused documentation requirements.
Independent evaluations coordinated through REE Medical provide detailed, objective clinical documentation that meets VA formatting standards. These evaluations include comprehensive functional assessments that measure how flat feet affects daily activities, work capacity, and quality of life.
Veterans can learn more about coordinating VA-compliant DBQs and independent medical evaluations by contacting REE Medical for an informational consultation. REE Medical’s team explains the documentation coordination process and connects veterans with independent, licensed medical providers.

Final Thoughts
Successfully obtaining appropriate VA compensation for flat feet requires understanding the medical complexities of pes planus, strategic claim development, and comprehensive documentation that captures the condition’s full impact on daily functioning. Flat feet represents more than just a structural foot problem—it’s a condition that can significantly impact quality of life, work capacity, and overall well-being.
Military service may have caused or worsened this condition, and veterans deserve fair compensation for its ongoing effects. VA ratings focus heavily on functional limitations rather than just medical diagnoses, making thorough documentation of how flat feet affects daily activities important for obtaining accurate ratings.
The claims process can be complex, but with proper preparation, comprehensive medical evidence, and strategic timing, veterans can maximize their chances of receiving appropriate compensation. Veterans who feel they may have received inadequate ratings should understand how to challenge low VA ratings to pursue the full compensation they deserve for their service-connected flat feet condition.

Disclosure
DISCLAIMER: REE Medical, LLC is not a Veterans Service Organization (VSO) or a law firm and is not affiliated with the U.S. Veterans Administration (“VA”). Results are not guaranteed, and REE Medical, LLC makes no promises. REE Medical’s staff does not provide medical advice or legal advice, and REE Medical is not a law firm. Any information discussed, such as, but not limited to, the likely chance of an increase or service connection, estimated benefit amounts, and potential new ratings, is solely based on past client generalizations and not specific to any one patient. The doctor has the right to reject and/or refuse to complete a Veteran’s Disability Benefit Questionnaire if they feel the Veteran is not being truthful. The Veteran’s Administration is the only agency that can make a determination regarding whether or not a Veteran will receive an increase in their service-connected disabilities or make a decision on whether or not a disability will be considered service-connected. This business is not sponsored by, or affiliated with, the United States Department of Veterans Affairs, any State Department of Military and Veterans Affairs, or any other federally chartered veterans service organization.