VA Form 21-686c: The Hidden Money You’re Missing from Your VA Benefits
VA Form 21-686c is one of the an important form for updating dependent information that can affect VA disability compensation. When family structure changes through marriage, divorce, birth, adoption, or guardianship, updating dependent information with the VA ensures that benefits accurately reflect current household circumstances. Understanding when and how to file this form allows veterans to ensure benefits accurately reflect household circumstances and helps avoid delays or inaccuracies in benefit payments.
The VA Form 21-686c serves as the VA’s official method for verifying and updating dependent status, directly influencing monthly payment calculations. Because the VA requires precise documentation, missing details or outdated records can result in reduced compensation or delayed adjustments. With recent guidance emphasizing that many veterans have not updated their dependents in 2025, timely submission helps keep VA records current. Proper documentation and a clear understanding of dependent eligibility allow veterans to receive the correct compensation while keeping their file current and accurate.
This comprehensive guide explains the fundamentals of VA Form 21-686c, provides step-by-step completion guidance, outlines submission methods and timelines, and addresses common issues veterans encounter during the process.
TL;DR
- VA Form 21-686c adds or removes dependents from disability compensation, which may affect monthly compensation depending on VA determination
- Filing within one year of marriage or birth/adoption may allow retroactive payment subject to VA rules to the event date
- Online submission through VA.gov provides commonly processed within published VA timelines
- Missing or inconsistent documentation causes the majority of processing delays and rejections
- Dependent benefit amounts are based on VA disability ratings, making medical documentation relevant to VA evaluations
- Special circumstances like stepchildren, disabled adult children, or foreign documents require additional verification steps
Understanding VA Form 21-686c Fundamentals
VA Form 21-686c serves as the form used to update dependent information for VA benefit review for family members. This “Declaration of Status of Dependents” operates under federal law (38 U.S.C. §§ 5901–5905) and may affect disability payments and eligibility for certain benefits. Understanding its purpose and legal framework allows veterans to receive appropriate benefits while maintaining compliance with VA reporting requirements.
According to recent updates from FingerLakes1.com, veterans receiving disability compensation could be may not reflect updated family circumstances if their family status has changed in 2025. Whether through marriage, the birth of a child, or supporting a student, updating dependent information with the VA can increase monthly benefits.
Why Accurate Dependent Reporting Matters
The VA Form 21-686c Declaration of Status of Dependents functions as the official communication channel with the VA about family changes, ensuring VA records are accurate and proper dependent coverage. Its impact extends beyond monthly payments to include healthcare access and educational opportunities for family members.
The Legal Foundation Behind Benefits
Federal statutes establish veteran entitlement to dependent benefits while requiring accurate family status maintenance. This legal framework protects both veterans and the VA system through structured reporting requirements.
The form draws its authority from Title 38 of the U.S. Code, specifically sections 5901 through 5905. These statutes establish entitlement to additional compensation for dependents while creating the framework for proper documentation.
This legal structure serves as a protective framework. It ensures the VA evaluates legitimate dependent information while maintaining system integrity through structured reporting requirements. Veterans are required to maintain accurate records, and in return, additional compensation is available for qualifying family members.
How Dependent Status Can Affect Compensation
Adding dependents can substantially increase monthly disability compensation, with amounts varying based on disability rating percentage and number of dependents. Understanding these financial impacts emphasizes the importance of timely and accurate form submission.
The financial impact depends on disability rating. Amounts vary based on VA-published compensation tables and disability rating. These amounts can total thousands of dollars annually.
Disability rating percentage determines the exact amounts. A veteran with a 70% rating receives significantly more for dependents than someone at 30%. The VA publishes these rates annually, and they typically increase with cost-of-living adjustments.
VA disability ratings determine dependent compensation amounts. For detailed information about how ratings work, veterans can explore resources about 100% VA disability rating to understand the full scope of benefits available at higher rating levels.
The retroactive benefit provision allows recovery of up to a year of missed payments when filing within the deadline, making timely submission financially significant.
Monthly Dependent Compensation by Rating:
| Disability Rating | Spouse Compensation | Each Child | Total for Family of 4 |
| 30% | $171 | $75 | $321 |
| 50% | $264 | $75 | $414 |
| 70% | $419 | $75 | $569 |
| 100% | $755 | $248 | $1,251 |
Dependent Eligibility for Healthcare and Education Programs
VA determinations may establish dependent eligibility to CHAMPVA healthcare coverage and educational benefits, making accurate completion crucial for comprehensive family welfare beyond just monthly compensation.
Healthcare coverage through CHAMPVA can represent significant value annually. Dependents gain access to medical, dental, and vision coverage that provides comprehensive protection. The educational benefits extend to vocational training, college tuition assistance, and specialized programs.
A single emergency room visit or semester of college tuition can cost more than a year’s worth of dependent compensation.
Who Qualifies and What Documentation Is Required
Understanding dependent qualification criteria and required documentation prevents processing delays and ensures successful applications. Different dependent categories have specific requirements that must be met with proper supporting evidence.
Learning how to add a dependent to VA disability benefits requires understanding the specific documentation each category of dependent requires.
Example: Consider John, a 60% disabled veteran who recently married Sarah. By filing Form 21-686c with their marriage certificate within one year of their wedding date, John can receive an additional $371 monthly ($4,452 annually) in dependent compensation retroactive to their marriage date.
Spouse Eligibility Requirements
Spouses must be legally married to the veteran, with marriage certificates and divorce decrees from previous marriages serving as primary documentation requirements for establishing eligibility.
Marriage certificates form the cornerstone of spouse dependency documentation. The VA requires certified copies, not photocopies or smartphone photos. If either spouse was previously married, divorce decrees or death certificates from those prior relationships become mandatory.
Common-law marriages present additional complexity. Some states recognize them, others don’t. The VA follows state law where the marriage occurred, which may require additional documentation proving the relationship meets legal standards.
Military marriages overseas require extra attention. Foreign marriage certificates need translation and authentication through appropriate consular services. This process takes longer, so planning accordingly is important.
Children’s Qualification Requirements
Children under 18, or under 23 if enrolled in school, qualify as dependents requiring birth certificates, adoption papers, or school enrollment verification as supporting documentation.
Birth certificates establish the parent-child relationship for biological children. Adoption papers serve the same purpose for adopted children, but they must show finalized adoption, not just placement or foster care arrangements.
School enrollment becomes crucial for children over 18. The VA requires official transcripts or enrollment verification letters from accredited institutions. Summer breaks don’t disqualify students, but gaps between semesters might trigger reviews.
Stepchildren present unique challenges. Proof of marriage to their biological parent plus evidence of financial support is required. Court orders establishing custody or support obligations strengthen these claims significantly.
When Parents Become Dependents
Parents may qualify if they receive financial support from the veteran, requiring income statements and dependency affidavits as supporting documentation to prove the financial relationship.
Parent dependency claims require proving financial support. The VA evaluates whether the veteran provides more than half of their support, which means detailed financial documentation. Bank statements, receipts, and signed affidavits all play important roles.
Income thresholds matter for parent dependency. If parents have substantial income from Social Security, pensions, or other sources, proving dependency becomes more challenging. Documentation must demonstrate that veteran contributions exceed other income sources.
Medical expenses often factor into the calculation. If a veteran pays for parent healthcare, medications, or assisted living costs, these expenses count toward the support calculation. Maintaining detailed records of all payments supports these claims.

Recognizing When to File
Understanding filing triggers ensures veterans can receive appropriate benefits and maintain compliance with VA reporting requirements. Different life events create specific deadlines and opportunities.
Life Events That Trigger Filing
Marriage and new child events require filing within one year to receive retroactive benefits to the event date, subject to VA effective-date rules.
Marriage creates an immediate filing opportunity. Veterans have one year from the marriage date to file and receive retroactive benefits back to that date. After this deadline, benefits typically start from when the VA receives the form.
Birth or adoption of children follows the same one-year rule. The clock starts ticking from the birth date or finalization of adoption. Filing before the event occurs results in rejection, so timing matters.
Military deployments can complicate timing. If deployment occurs when a qualifying event happens, special provisions may extend filing deadlines. Documenting deployment status and communicating with the VA about timing issues is important.
When Dependents Need to Be Removed
Divorce and child age-out situations require prompt notification to prevent overpayment issues and potential debt collection, making timely dependent removal as important as addition.
Divorce immediately disqualifies former spouses from dependent status. The VA requires prompt notification. Continued payments after divorce create debt that the VA will eventually collect, often through benefit reductions.
Children aging out of eligibility need removal too. When they turn 18 (or 23 if in school), their dependent status ends. Graduation, dropping out, or extended breaks from school all trigger removal requirements.
Death of a dependent requires immediate notification. While emotionally difficult, failing to report deaths can create overpayment situations that add financial stress during a difficult time.

Step-by-Step Form Completion Process
Proper form completion requires systematic preparation, careful attention to detail, and understanding of VA-specific requirements. This process involves document assembly, section-by-section completion, and thorough review before submission to avoid delays or rejections.
Understanding how to fill out VA Form 21-686c correctly from the start prevents most common processing issues.
Getting Paperwork Ready
Successful form submission begins with comprehensive preparation, ensuring all required documents are current, complete, and properly formatted before starting the application process.
Essential Document Checklist
Gathering marriage certificates, birth certificates, Social Security cards, and relevant court documents before starting streamlines the completion process and prevents mid-application delays.
Document Preparation Checklist:
- Certified marriage certificate (not photocopy)
- Divorce decrees from all previous marriages
- Birth certificates for all children
- Social Security cards for all dependents
- School enrollment verification (if applicable)
- Death certificates (if removing deceased dependents)
- Court custody orders (for stepchildren)
- Military discharge papers (DD-214)
Starting with certified copies of everything is essential. The VA doesn’t accept photocopies for most documents, so ordering certified copies from issuing agencies takes priority. This process can take weeks.
Marriage certificates must be certified copies from the county or state where the marriage occurred. For overseas marriages, certificates need authentication by the appropriate consular office. Keeping originals safe and submitting only certified copies protects important documents.
Birth certificates for children need to be certified copies showing both parents’ names. Hospital-issued certificates often lack required information, so ordering official copies from state vital records offices may be necessary.
Social Security cards or official letters from the Social Security Administration work for proving Social Security numbers. Screenshots of online accounts don’t meet VA standards.
Double-Checking Information
Cross-referencing all personal information, dates, and Social Security numbers against official documents prevents errors that could significantly delay processing times.
Verifying every name exactly as it appears on official documents is important. Middle initials, suffixes, and hyphenated names must match perfectly. Even small discrepancies can trigger verification delays.
Dates require special attention. Using the MM/DD/YYYY format consistently throughout the form helps ensure accuracy. Birth dates, marriage dates, and other significant dates must match supporting documents exactly.
Social Security numbers need verification against official documents. Transposed digits are common errors that create processing complications. Double-checking each number against the actual Social Security card or official letter prevents these issues.

Completing Each Section Accurately
Each form section serves specific purposes and requires particular attention to formatting, completeness, and accuracy standards to ensure smooth processing.
Example: Maria, a 40% disabled veteran, needs to add her newborn son Miguel. She completes Section III with Miguel’s full name “Miguel Antonio Rodriguez,” his birth date “03/15/2024,” Social Security number, and selects “biological child” as the relationship type, ensuring all information matches his certified birth certificate exactly.
The Veteran Information Section
Complete all veteran identification fields using exact information from the VA file, including full legal name, Social Security number, and VA file number for proper account matching.
Full legal name must match VA records exactly. If legal name changes have occurred since establishing the VA file, updating those records first prevents form rejection due to name mismatches.
VA file numbers appear on most VA correspondence. If this number isn’t readily available, Social Security numbers work as alternative identifiers. However, having the VA file number speeds up processing.
When dealing with complex claim situations, having proper documentation becomes essential. Veterans facing challenges with their claims often benefit from understanding common VA disability filing mistakes to avoid similar issues with dependency forms.
Service information requires accuracy too. Branch of service, service dates, and discharge status must match military records. Approximations don’t work—the VA cross-references everything.
Dependent Information That Gets Results
Providing complete dependent details including full names, birth dates, Social Security numbers, and relationship to veteran ensures consistency with supporting documents and prevents verification delays.
Each dependent needs their own section with complete information. Full legal names, not nicknames or shortened versions, are required. Birth dates must match supporting documents exactly.
Relationship descriptions need precision. “Spouse,” “child,” “stepchild,” or “adopted child” have specific meanings to the VA. Choosing the correct relationship type based on actual legal relationship is essential.
Social Security numbers for dependents are mandatory. If a dependent doesn’t have one, applying for one before submitting the form is necessary. The VA cannot process claims without this information.
The Critical Certification Section
The certification section requires careful review of all entered information and understanding that false statements carry legal penalties under federal law, making accuracy essential.
Reading the certification statement completely before signing is important. The signature certifies that all information is true and complete to the best of knowledge. False statements can result in serious consequences.
Signatures must match the name used throughout the form. Electronic signatures are acceptable for online submissions, but they must be actual signatures, not just typed names.
Dating the form on the day of signing, not when form completion started, creates an accurate official record and affects processing timelines.
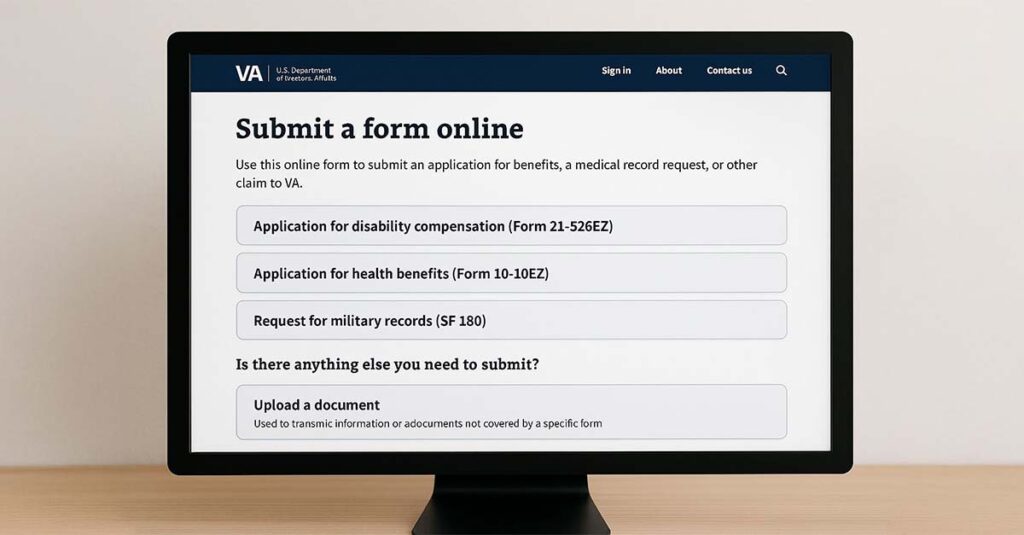
Submission Methods and Processing Timeline
The VA offers multiple submission channels with distinct advantages, processing times, and tracking capabilities. Understanding these options and expected timelines helps veterans plan effectively and monitor application progress.
For those who need to download VA Form 21-686c, the form is available through VA.gov.
Choosing a Submission Strategy
Different submission methods offer varying advantages in terms of processing speed, confirmation, and tracking capabilities, allowing veterans to choose based on their preferences and circumstances.
Digital Submission: Online Submission Option
Online submission through VA.gov provides immediate confirmation, faster processing, and real-time status tracking through veterans’ online accounts, making it the preferred method for most situations.
VA.gov submission provides immediate confirmation and a tracking number. Veterans know within seconds that their form reached the VA successfully. This eliminates uncertainty about mail delivery and provides peace of mind.
Uploading supporting documents directly to the system allows the VA to access everything immediately, reducing processing time significantly. Digital documents are also less likely to get lost or damaged compared to mailed papers.
Real-time status updates keep veterans informed throughout the process. Logging into accounts anytime allows checking progress, seeing if additional information is needed, or confirming when processing is complete.
Traditional Methods Remain Available
Mail and in-person options remain available for veterans preferring paper processes or lacking digital access, though processing times are typically longer than online submissions.
Mailing forms to the appropriate VA regional office remains an option. Using certified mail with return receipt confirms delivery. Keeping copies of everything sent protects against lost documents.
In-person submission at VA regional offices or veterans service organizations provides face-to-face assistance. Staff can review forms for completeness and answer questions before submission.
Fax submission works for some situations, but calling ahead to confirm the receiving office accepts faxed forms is advisable. Not all VA offices process faxed dependency claims.
Submission Method Comparison:
| Submission Method | Processing Time | Confirmation | Tracking | Best For |
| Online (VA.gov) | 30-60 days | Immediate | Real-time | Most veterans |
| 60-90 days | Receipt only | Limited | No internet access | |
| In-person | 45-75 days | Immediate | Phone/mail | Complex cases |
| Fax | 60-90 days | Call to confirm | Phone only | Urgent situations |
What to Expect During Processing
Understanding typical processing timeframes and available tracking methods helps veterans manage expectations and identify when follow-up action may be necessary.
Timeline Reality Check
Most applications process within 30-60 days, though complex cases or missing documentation can extend timelines significantly, requiring patience and proactive communication.
Standard processing takes 30-60 days for complete applications with all required documentation. This timeframe starts when the VA receives the form, not when it’s mailed.
Complex cases take longer. Multiple dependents, foreign documents, or unusual circumstances can extend processing to 90+ days. The VA may need additional verification or documentation.
Incomplete applications get delayed indefinitely. Missing documents or unclear information triggers requests for additional evidence. These requests reset the processing clock, so completeness matters significantly.
Staying Informed About Status
Veterans can monitor application status through VA.gov, by phone, or through written correspondence, with the VA providing updates at key processing milestones.
Online tracking through VA.gov provides the most current information. Status updates appear in real-time as applications move through different processing stages.
Phone inquiries work but expect wait times. The VA’s customer service lines handle high call volumes, especially during peak filing periods. Having the VA file number ready speeds up these calls.
Written correspondence from the VA arrives at key milestones. Confirmation when applications are received, notifications if additional information is needed, and final decisions when processing is complete all arrive by mail.

Troubleshooting and Common Issues
Anticipating potential problems and understanding resolution strategies helps veterans navigate challenges and avoid common pitfalls that delay benefit changes. Most issues stem from documentation problems or information inconsistencies.
Avoiding the Most Common Mistakes
Recognizing frequent application errors and their solutions prevents delays and reduces the need for resubmission or additional documentation requests.
Documentation Problems That Delay Applications
Missing or unclear supporting documents represent the most common cause of delays, requiring veterans to provide certified copies or additional verification to meet VA standards.
Uncertified copies get rejected automatically. The VA requires certified copies for most supporting documents, not regular photocopies or scanned images. This requirement catches many veterans off guard.
Illegible documents create verification problems. Faded, torn, or poorly copied documents can’t be processed. If original documents are in poor condition, requesting new certified copies from the issuing agency is necessary.
Foreign language documents need official translation. The VA doesn’t translate documents internally, so certified translations from qualified translators are required. This adds time and expense to applications.
Missing pages or incomplete documents trigger requests for additional evidence. Birth certificates without parent information, marriage certificates without official seals, or partial court orders all create processing delays.
Example: Robert submitted his form with a photocopy of his marriage certificate instead of a certified copy. The VA requested proper documentation, delaying his spouse’s benefits by three months until he obtained and resubmitted the certified marriage certificate.
Information Mismatches That Trigger Reviews
Discrepancies between form information and supporting documents trigger review processes that can significantly extend processing times and require additional verification steps.
Name variations between documents cause verification delays. If a marriage certificate shows “Robert” but the VA file shows “Bob,” the VA needs clarification. Consistency across all documents prevents these issues.
Date discrepancies trigger manual reviews. If a form shows one birth date but the birth certificate shows another, processing stops until the discrepancy is resolved. Double-checking all dates before submission prevents this.
Social Security number errors create major problems. Transposed digits or incorrect numbers can link applications to wrong records. These errors require extensive verification to correct.

When Things Go Wrong
When applications are reviewed or adjusted by the VA, veterans have specific rights and procedures for seeking correction or appeal through established VA review processes.
Veterans experiencing claim denials can explore options for requesting VA review options. Resources on how to challenge a low VA rating provide strategies that apply to dependency determinations as well.
Administrative Review Options
Veterans can request reconsideration of dependency determinations through formal review processes that examine both the application and supporting evidence for potential errors or oversights.
Requesting reconsideration when the VA may have made an error involves submitting a written request explaining the disagreement with the decision and providing any additional evidence that supports the position.
Higher-level reviews involve senior VA personnel who weren’t involved in the original decision. These reviews can overturn previous decisions if errors are identified in the application of law or policy.
Supplemental claims allow submission of new evidence that wasn’t available during the original review. Medical records, court documents, or other supporting materials can strengthen cases significantly.
Getting Professional Help
Complex dependency cases may benefit from professional assistance, particularly when dealing with unusual family situations or disputed documentation requirements that exceed typical processing procedures.
Veterans service organizations provide free assistance with dependency claims. These organizations have trained representatives who understand VA procedures and can help navigate complex situations.
Private attorneys specialize in VA law when cases become particularly complex. Legal representation becomes valuable when dealing with unusual family situations, disputed paternity, or international complications.
Accredited agents offer middle-ground assistance between free VSO services and private attorneys. These professionals charge fees but provide specialized expertise in VA claims processing.

Advanced Considerations and Special Circumstances
Complex family situations and unique circumstances require specialized approaches to VA Form 21-686c completion, often involving additional documentation and extended processing procedures that go beyond standard dependency claims.
Navigating Complex Family Dynamics
Certain dependent situations fall outside standard categories and require additional consideration and documentation to establish eligibility under VA regulations.
Stepchildren and Adoption Complexities
Stepchildren require proof of marriage to their biological parent and evidence of financial support, while adopted children need finalized adoption decrees and court documentation showing legal parent-child relationships.
Stepchildren create unique documentation challenges. Marriage certificates to their biological parent plus evidence of financial support are required. Court-ordered support agreements, school records listing the veteran as a parent, or medical insurance coverage all help establish this relationship.
Adoption timing matters significantly. The VA recognizes adopted children only after finalization, not during placement or foster care periods. Adoption decrees must show completed legal proceedings, not just intent to adopt.
International adoptions require additional verification. Foreign adoption decrees need authentication through appropriate consular services, and proving the adoption meets U.S. legal standards may be necessary.
Adult Children with Disabilities
Adult children with disabilities that began before age 18 may qualify for continued dependency, requiring medical evidence and disability onset documentation to prove eligibility beyond normal age limits.
Disability onset before age 18 is the key requirement. Medical records must clearly establish that the disabling condition existed before the child’s 18th birthday. Hospital records, school special education files, or early medical diagnoses all serve as evidence.
Continuous disability from childhood through adulthood needs documentation. Gaps in medical care or periods of improvement might complicate these claims. Comprehensive medical records showing ongoing treatment strengthen cases.
Severity standards mirror Social Security disability criteria. The condition must prevent substantial gainful employment, not just create limitations. Medical opinions about functional capacity become crucial evidence.

International and Military-Specific Challenges
Veterans with dependents overseas or in military-specific circumstances face unique documentation and verification challenges that require specialized handling and additional processing time.
According to FingerLakes1.com, recent guidance emphasizes the importance of proper documentation for non-traditional or international marriages, which may require additional supporting documents like affidavits, marriage certificates, or birth records for overseas dependents.
Foreign Document Authentication
International documents require translation and authentication through appropriate consular services, adding complexity and time to the verification process while meeting VA standards.
Embassy authentication becomes necessary for foreign marriage certificates, birth certificates, and other vital documents. Each country has different procedures, and processing times vary significantly.
Certified translations must come from qualified translators. The VA doesn’t accept informal translations. Professional translation services familiar with legal documents provide the required certification.
Apostille certification simplifies authentication for countries participating in the Hague Convention. This international certification process is faster than traditional embassy authentication but isn’t available for all countries.
Military Family Considerations
Active-duty spouses and military children may have special documentation requirements and benefit coordination considerations that affect processing and eligibility determinations.
Active-duty spouses create benefit coordination considerations. Military pay and allowances might affect dependency calculations, and dual military couples face additional complexity in determining primary and secondary benefits.
Military children born overseas often have different documentation. Consular Reports of Birth Abroad serve as birth certificates for children born to U.S. citizens overseas, but the VA may require additional verification.
Understanding how military service affects benefit eligibility helps veterans navigate complex situations. Resources on benefits for spouses and dependents of disabled veterans provide essential context for military families.
Deployment-related timing issues can affect filing deadlines. Special provisions may extend normal filing periods when military duties prevent timely submission, but documenting these circumstances clearly is important.
Benefit Coordination Complexities
Veterans receiving other federal benefits should understand how dependent additions might affect Social Security, military retirement, or other government compensation programs to avoid conflicts or overpayments.
Social Security coordination becomes important for veterans receiving both VA disability and Social Security benefits. Adding dependents to VA benefits doesn’t automatically add them to Social Security, requiring separate applications.
Military retirement pay coordination affects veterans receiving both military retirement and VA disability compensation. Dependent benefits may be available through both systems, but coordination rules prevent duplicate benefits.
Federal employee benefits create additional coordination requirements. Veterans working for federal agencies may have dependent coverage through multiple systems, requiring careful coordination to optimize benefits without creating conflicts.

How REE Medical Supports Your VA Benefits Journey
While REE Medical cannot file VA Form 21-686c or provide direct assistance with dependency claims, our services complement the broader VA benefits process by coordinating independent medical documentation that may be reviewed by the VA during disability evaluations, which the VA may consider when determining compensation levels.
The connection between disability rating and dependent benefits is straightforward— VA disability ratings are used to calculate dependent compensation amounts. When veterans work to establish or increase their disability ratings, medical documentation may be part of the VA’s evaluation process for the monthly compensation that supports dependent needs.
REE Medical operates under a strict compliance framework ensuring complete neutrality and adherence to federal regulations (38 U.S.C. §§ 5901–5905). REE Medical does not prepare, present, or submit VA disability claims and does not provide legal or representational services. Instead, the focus remains on coordinating independent, objective medical evaluations and documentation within full legal and ethical boundaries.
Strong medical evidence forms the foundation of disability evaluations. Veterans seeking to understand the documentation process can benefit from learning about the importance of medical evidence in VA disability claims before pursuing dependent benefits.
REE Medical connects veterans with independent, licensed medical professionals for comprehensive evaluations when establishing or increasing disability ratings. These objective medical assessments provide the foundation for accurate disability evaluations, which may be reviewed by the VA in determining disability evaluations once Form 21-686c is processed.
Through complimentary consultations, veterans can explore whether additional medical documentation might help them understand available medical documentation options.
Final Thoughts
Filing VA Form 21-686c correctly can add hundreds of dollars monthly to disability compensation while opening doors to healthcare and educational benefits for family members. The key lies in thorough preparation, accurate documentation, and understanding the VA’s specific requirements.
The complexity of this process should not discourage veterans from pursuing benefits their families may be entitled to receive. Starting by gathering documents early, double-checking all information for accuracy, and choosing the submission method that works best for individual situations creates the foundation for successful applications. The VA applies effective-date rules when reviewing dependency updates.
Veterans experiencing challenges with their claims should understand available resources. Information about common challenges veterans face in disability advocacy highlights support options that can help throughout the benefits journey.
When complications arise—and they sometimes do—resources exist to help navigate the process. Whether through veterans service organizations, legal assistance, or administrative reviews, options exist for resolving problems and securing family benefits.
Disability ratings directly impact how much additional compensation veterans receive for dependents, making strong medical evidence essential for family financial security.
Disclosure
DISCLAIMER: REE Medical, LLC is not a Veterans Service Organization (VSO) or a law firm and is not affiliated with the U.S. Veterans Administration (“VA”). Results are not guaranteed, and REE Medical, LLC makes no promises. REE Medical’s staff does not provide medical advice or legal advice, and REE Medical is not a law firm. Any information discussed, such as, but not limited to, the likely chance of an increase or service connection, estimated benefit amounts, and potential new ratings, is solely based on past client generalizations and not specific to any one patient. The doctor has the right to reject and/or refuse to complete a Veteran’s Disability Benefit Questionnaire if they feel the Veteran is not being truthful. The Veteran’s Administration is the only agency that can make a determination regarding whether or not a Veteran will receive an increase in their service-connected disabilities or make a decision on whether or not a disability will be considered service-connected. This business is not sponsored by, or affiliated with, the United States Department of Veterans Affairs, any State Department of Military and Veterans Affairs, or any other federally chartered veterans service organization.