VA Disability Rating Increase: What Veterans Use to Unlock Higher Compensation
Veterans often find that their VA disability ratings don’t reflect the true impact of their service-connected conditions, which may not always reflect current symptom severity. This comprehensive guide explores the evaluation system, the importance of thorough medical documentation, and how the VA assesses conditions for rating increases. Whether a condition has worsened over time or an initial rating didn’t capture the full severity of a disability, understanding this process helps veterans understand how the VA evaluates requests for increased ratings
VA disability compensation rates are updated annually based on cost-of-living adjustments set by federal law. Veterans should reference the VA’s published rate tables each year to understand how monthly compensation amounts change over time
Additional resources—such as information about increase claims—are also available to support veterans along the way.
TL;DR
- VA disability rating increases are available when conditions worsen or initial ratings were inadequate, which may affect monthly compensation depending on VA evaluation
- The VA’s decision depends on comprehensive medical evidence that demonstrates functional limitations and symptom severity using VA-specific criteria
- Timing rules may affect effective dates and how the VA applies increased ratings
- Independent medical evaluations can provide additional clinical documentation for VA review
- The appeals process offers multiple pathways when initial increase requests are denied, each following different VA review processes

Understanding the VA Rating Increase System
The VA’s disability rating system operates on a percentage scale that directly correlates to monthly compensation amounts. Many veterans don’t realize they can seek reevaluation when conditions deteriorate or when initial ratings may not have captured the full severity of their disabilities. Understanding the different types of increase requests, rating criteria, and timing considerations forms the foundation for navigating this complex system.
Veterans seeking to understand their current situation can first learn what determines a VA rating before pursuing an increase, as this foundational knowledge helps identify the strongest approach for specific circumstances.
Common Situations That Lead Veterans to Request Re-Evaluation
Veterans have multiple avenues for pursuing rating increases depending on their specific circumstances, each requiring distinct approaches and evidence standards. Whether a condition has genuinely worsened since the last evaluation or an initial rating didn’t capture the true severity of the disability, understanding these pathways helps in understanding how the VA evaluates different situations.
When a Condition Has Actually Gotten Worse
Requesting an increase based on condition deterioration requires demonstrating that symptoms have become more severe, frequent, or debilitating since the last VA rating decision, supported by recent medical evidence and functional impact documentation.
Service-connected disabilities don’t remain static. Conditions evolve, symptoms intensify, and what might have been manageable years ago could now significantly impact daily life. The VA recognizes this reality through increase requests for worsened conditions.
Documentation becomes crucial in these situations. Medical records showing progression of symptoms, new treatments or medications, increased frequency of flare-ups, or additional complications all serve as evidence. The key isn’t just proving a condition exists—it’s demonstrating measurable deterioration from the previous rating period.
Functional changes also matter significantly. A veteran who could work full-time when initially rated at 30% but now struggles to maintain employment due to worsening symptoms has experienced real-world impacts that often carry significant weight in VA evaluations.
Example: A veteran initially rated 30% for PTSD in 2019 began experiencing increased nightmares, panic attacks, and social isolation by 2024. Their treating psychiatrist documented medication increases from 50mg to 150mg of sertraline, new prescriptions for sleep aids, and notes about the veteran’s difficulty maintaining employment due to anxiety. These progressive changes in treatment and function were part of the evidence the VA reviewed when assigning a 70% rating.
When an Initial Rating May Not Have Been Accurate
When an original VA rating doesn’t accurately reflect a disability’s true impact, veterans can pursue an increase by presenting evidence that demonstrates the condition’s severity, focusing on symptoms and limitations that may have been overlooked or undervalued in the initial evaluation.
Sometimes the initial rating process doesn’t capture the full scope of a condition’s impact, especially when comprehensive medical records weren’t available or when key symptoms weren’t fully assessed during the C&P examination.
This type of increase request focuses on evidence that demonstrates the condition’s true severity. Medical records, detailed statements about the condition’s historical impact, and medical opinions that interpret existing evidence through the lens of VA rating criteria can all support a VA disability rating increase request.
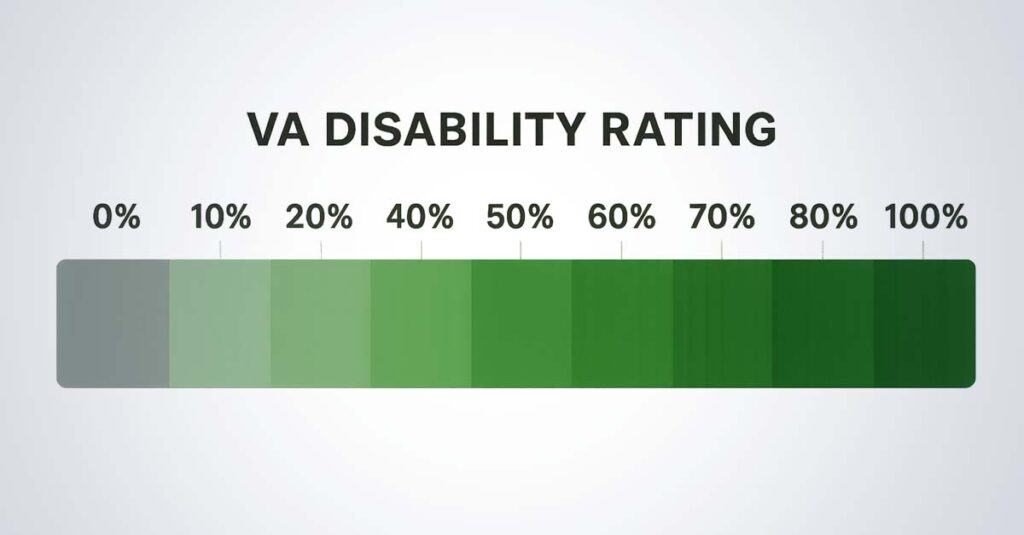
How the VA Actually Assigns Rating Percentages
The VA uses a structured percentage system from 0% to 100% based on specific criteria outlined in their Schedule for Rating Disabilities, where each increment represents increasingly severe symptoms and functional limitations that directly determine monthly compensation amounts.
Decoding the Rating Criteria That Matter
Each disability has detailed rating criteria that focus on symptom frequency, severity, and functional impact rather than just diagnosis, requiring veterans to understand these specific benchmarks when gathering evidence for their requests.
The VA doesn’t simply look at a diagnosis and assign a percentage. Each condition has specific criteria outlined in the Schedule for Rating Disabilities (38 CFR Part 4). These criteria focus on functional limitations, symptom frequency, and severity levels.
For mental health conditions, the VA evaluates factors like occupational impairment, social functioning difficulties, and cognitive symptoms. Physical conditions might be evaluated based on range of motion limitations, pain levels, or impact on daily activities.
Understanding these criteria helps in framing evidence appropriately. Instead of simply stating “my back hurts,” documentation of specific limitations like “unable to lift more than 10 pounds” or “requires frequent position changes every 30 minutes” provides the VA with concrete information for evaluation.
The difference between rating levels often comes down to specific thresholds. A 30% mental health rating might involve “occasional decrease in work efficiency,” while 50% involves “reduced reliability and productivity.” Knowing these distinctions helps in presenting evidence that clearly addresses higher rating criteria.
VA Rating Criteria Overview:
| Rating Level | Mental Health Criteria | Physical Criteria Example |
| 10% | Mild symptoms, little impairment | Slight limitation of motion |
| 30% | Occasional decrease in work efficiency | Moderate limitation of motion |
| 50% | Reduced reliability and productivity | Marked limitation of motion |
| 70% | Deficiencies in most areas | Severe limitation of motion |
| 100% | Total occupational impairment | Complete loss of function |
Timing Considerations in VA Rating Reviews
Rating increase requests involve careful consideration of timing factors, including protection periods for existing ratings, optimal filing windows based on medical developments, and effective date implications that can significantly impact retroactive compensation amounts.
Understanding Protected Ratings and Potential Considerations
Veterans with ratings held for certain time periods may have protection against reductions under VA rules, but requests for increases can sometimes trigger comprehensive reviews. Understanding these rules allows for careful assessment before proceeding.
According to VA regulations, ratings held for 20 years or more are generally protected from reduction except in cases of fraud. Ratings held for 10+ years have stronger protection and require clear evidence of improvement for reduction.
Veterans with ratings held for less than 5 years may want to be aware of how VA review rules apply and consider how VA regulations apply to review requests of a comprehensive review. Some veterans choose to review VA protection rules before filing.
Veterans rated at 100% face unique considerations. Total disability ratings based on unemployability (TDIU) have different protection rules than 100% schedular ratings under VA regulations, and understanding these distinctions is important.
Timing Considerations for Effective Dates
The effective date of an increase request determines when higher compensation begins, which the VA applies based on regulatory criteria while ensuring sufficient medical evidence exists to support the request.
Per VA guidance, the effective date is generally either the date the request was filed or the date the condition worsened—whichever is later. This creates a consideration: the VA determines effective dates based on evidence and filing date
Medical records play a crucial role in effective date determination. If medical documentation from several months prior clearly shows symptom progression, that evidence may support an earlier effective date based on when the worsening was documented.
Seasonal patterns also matter for some conditions. Conditions that worsen during specific times of year benefit from filing during a documented flare-up period, supported by medical records.

General Considerations When Requesting a Rating Increase
Successfully obtaining a VA disability rating increase requires a methodical approach that begins with thorough preparation and assessment, followed by strategic development of compelling medical evidence, and concludes with proper submission and active follow-up throughout the review process.
Before beginning the increase process, veterans can understand the fundamentals by learning how to request a VA disability rating increase to ensure they’re following proper procedures and timelines.
Preparing Medical Records Before Submitting a Request
Before submitting an increase request, conducting a comprehensive assessment of the current medical situation, gathering preliminary evidence, and evaluating whether pursuing an increase is supported by available medical documentation based on specific circumstances and available documentation are all important steps.
Conducting a Thorough Medical Records Review
Systematically reviewing all medical documentation since the last rating helps identify evidence of symptom progression, new treatments, hospitalizations, or functional limitations that support an increase request while revealing potential gaps that need addressing.
The process begins with gathering every piece of medical documentation since the last rating decision. This includes VA medical records, private healthcare visits, emergency room trips, specialist consultations, and prescription changes. Mental health counseling notes or physical therapy records often contain detailed functional assessments and should not be overlooked.
Creating a timeline of the condition’s progression helps identify patterns of worsening symptoms, increased medication dosages, new treatment modalities, or additional diagnoses related to service-connected conditions. Emergency room visits or hospitalizations carry particular weight as evidence of condition severity.
Provider notes that describe functional limitations are particularly valuable. Statements like “patient reports difficulty with prolonged standing” or “exhibits significant anxiety in social situations” provide concrete evidence for rating criteria. These observations from treating physicians often prove more valuable than test results alone.
Identifying gaps in the medical record that might need filling is also important. If symptoms have been managed without seeking treatment, recent medical documentation might strengthen the case before filing.
Medical Records Review Checklist:
- VA medical records from all facilities
- Private healthcare provider records
- Emergency room and urgent care visits
- Specialist consultation reports
- Mental health counseling notes
- Physical therapy evaluations
- Prescription medication changes
- Diagnostic test results
- Hospitalization records
- Workers’ compensation files (if applicable)
Documenting Real-World Functional Impact
Creating detailed records of how a condition affects daily activities, work performance, and quality of life provides crucial evidence that is considered by the VA during evaluation.
The VA evaluates how conditions affect daily life, not just diagnostic labels. Documenting specific functional limitations in detail—keeping a symptom diary noting frequency, severity, and impact of flare-ups—creates valuable evidence. Recording how the condition affects work performance, household tasks, social activities, and self-care provides concrete information for evaluation.
Specificity matters more than general statements. Instead of “I have trouble sleeping,” documentation such as “wake up 3-4 times nightly due to pain, requiring position changes, resulting in fatigue that affects concentration at work” gives the VA a clearer picture of the condition’s true impact.
Statements from family members or close friends about changes they’ve observed in functioning can corroborate reported limitations and provide additional perspective on the condition’s impact.
Work-related impacts deserve special attention. Documenting missed work days, reduced productivity, accommodation needs, or job changes necessitated by the condition often may be reviewed by the VA when assessing severity.
Example: A veteran with a 50% back injury rating documented that their condition worsened to the point where they could no longer perform their job as a construction supervisor. The evidence showed: missed 45 work days in six months due to back spasms, required a sit-stand desk accommodation, could no longer lift materials over 20 pounds, and eventually had to transfer to a desk job with 30% less pay. This comprehensive functional impact documentation was part of the record the VA reviewed when assigning a 70% rating.

Building Strong Medical Evidence
Strong medical evidence forms the cornerstone of successful increase requests, requiring comprehensive documentation from qualified medical professionals who understand VA rating criteria and can provide detailed assessments that clearly demonstrate a condition’s current severity and functional impact.
The Power of Independent Medical Examinations
Obtaining thorough medical evaluations from qualified physicians who specialize in VA disability assessments provides objective, detailed documentation that complements existing medical records and strengthens increase requests through comprehensive symptom assessment and functional analysis.
While treating physicians know their patients’ conditions well, they might not understand VA rating criteria or provide the detailed functional assessments the VA needs. Independent medical examinations from providers experienced in VA disability evaluations can supplement existing treatment records.
These examinations focus specifically on rating criteria rather than treatment planning. The examining physician assesses symptom frequency, severity, and functional impact using VA terminology and standards, documenting specific limitations that correspond to rating levels.
Choosing providers carefully matters. Physicians who understand the Schedule for Rating Disabilities and have experience with VA evaluations produce reports that are comprehensive, objective, and clearly document symptoms and functional impact using VA terminology.
The examination should be thorough and well-documented. A rushed 15-minute exam won’t provide the detailed assessment needed for a strong request. Quality independent medical examinations often take 45-60 minutes and result in comprehensive reports that address all relevant rating factors.
Understanding the role of professional medical evidence becomes clearer when veterans learn about the importance of medical evidence in VA disability evaluations, which explains how comprehensive documentation directly impacts evaluation outcomes.

Navigating the Submission Process
Proper submission involves completing the correct VA forms accurately, providing comprehensive supporting documentation, and maintaining active engagement throughout the review process to ensure the request receives thorough consideration and prompt resolution.
Completing VA Form 21-526EZ
The Application for Disability Compensation and Related Compensation Benefits must be completed accurately and thoroughly, ensuring all relevant conditions, evidence, and supporting documentation are properly identified and submitted to avoid delays or denials.
VA Form 21-526EZ serves as the formal request for a rating increase. Completing every section thoroughly and accurately is essential. In the remarks section, clearly explaining what has changed since the last rating and why an increase is warranted provides important context.
Listing all supporting evidence being submitted—including medical records, independent medical opinions, and lay statements—with specific date ranges and provider information helps the VA locate and review evidence properly.
According to the VA, submitting online through VA.gov when possible provides confirmation of receipt and allows easier tracking throughout the process. Keeping copies of everything submitted creates an important record.
Form 21-526EZ Completion Checklist:
- Personal information section completed accurately
- Service history details verified
- Current disability conditions listed with ratings
- New or worsened conditions clearly identified
- Supporting evidence inventory attached
- Remarks section explains reason for increase
- Contact information updated
- Electronic signature applied
- Confirmation receipt saved
- Copies of all documents retained
Staying Engaged Throughout the Review Process
Monitoring progress through official VA channels, responding promptly to requests for additional information, and maintaining organized records of all communications ensures requests move efficiently through the system while preserving rights and effective dates.
According to the VA, monitoring progress regularly through VA.gov or eBenefits is recommended. The VA might request additional information or schedule examinations, and prompt responses keep requests moving forward.
Responding to all VA requests quickly and completely is essential. Per VA guidance, failure to respond within specified timeframes can result in denial. If more time is needed, contacting the VA to request an extension rather than missing deadlines is advisable.
Keeping detailed records of all communications with the VA—noting dates, times, and content of phone calls, and saving copies of all correspondence—becomes crucial if an appeal is needed or if there are processing errors.

Overcoming Common Roadblocks and Denials
Veterans pursuing rating increases frequently encounter obstacles including insufficient medical evidence, inadequate VA examinations, and conflicting medical opinions that can affect their requests. Understanding these challenges and implementing proven solutions significantly improves outcomes while providing clear pathways forward when initial requests are denied through the appeals process.
Veterans facing denials can understand the top reasons VA disability claims get denied to avoid common pitfalls and strengthen their approach.
Solving Documentation and Evidence Problems
Insufficient or inadequate medical evidence represents a primary reason for denied increase requests, requiring strategic approaches to identify missing records, supplement inadequate examinations, and resolve conflicting medical opinions.
Tracking Down Missing Medical Records
Systematically identifying and obtaining missing treatment records, service medical records, and private healthcare documentation requires persistence and organization but often uncovers crucial evidence.
Missing medical records can significantly affect an otherwise strong request. Creating a comprehensive list of all healthcare providers seen since the last rating—including VA facilities, private doctors, specialists, emergency rooms, urgent care centers, and mental health providers—is an important first step.
Contacting each provider’s medical records department directly is necessary. Many have online portals for requesting records, while others require written requests. Being specific about date ranges and types of records needed helps ensure complete documentation. Different VA facilities don’t always share information seamlessly, so requesting records from each facility visited is important.
Military medical records present unique challenges. If service medical records are incomplete, contacting the National Personnel Records Center may help. Fire damage in 1973 destroyed many Army and Air Force records, but alternative sources might exist.
Records that might not initially seem relevant—such as physical therapy notes, occupational health evaluations, or workers’ compensation files—might contain valuable functional assessments that support a request.
Addressing Inadequate VA Examinations
When VA Compensation and Pension examinations are rushed, incomplete, or don’t adequately assess a condition’s severity, veterans can supplement the record with independent medical opinions and additional evidence to address these deficiencies.
VA C&P exams vary in quality. Some examiners are thorough and knowledgeable, while others may rush through appointments or lack expertise in specific conditions. When an examination seems inadequate, options exist.
First, reviewing the examination report carefully helps identify factual errors, missed symptoms, or inadequate assessment of functional limitations. If the examiner didn’t address key aspects of the condition or made obvious mistakes, documenting these deficiencies is important.
Per VA regulations, veterans cannot directly request a new C&P exam, but submitting additional evidence that highlights the inadequacies of the original examination is permitted. Independent medical opinions that address the gaps in the C&P exam can be particularly effective.
Submitting a detailed statement explaining what the C&P examiner missed or got wrong—being specific and factual rather than emotional, focusing on medical facts and functional limitations that weren’t properly assessed—can help address examination deficiencies.
Resolving Conflicting Medical Opinions
When medical providers disagree about a condition’s severity or impact, strategic presentation of evidence and expert medical opinions can help resolve conflicts by providing clear, well-reasoned explanations that address the disagreements directly.
Medical providers sometimes disagree about diagnosis, severity, or functional impact. When this happens in a record, the VA might deny an increase due to the conflicting evidence. Resolving these conflicts requires strategic thinking.
Identifying the specific points of disagreement between providers—whether it’s diagnosis, symptom severity, or functional limitations—helps in addressing it effectively.
Obtaining an independent medical opinion from a specialist who can review all the conflicting evidence and provide a reasoned explanation for why one opinion should be given more weight can be valuable. This expert can address the specific disagreements and explain their reasoning using medical literature and clinical experience.
The qualifications and expertise of the conflicting providers matter. Per VA guidance, a specialist’s opinion about their area of expertise typically carries more weight than a general practitioner’s assessment. Highlighting these qualifications when presenting evidence is important.
Sometimes conflicts arise from incomplete information. One provider might not have access to all medical records or might have examined during a period when symptoms were less severe. Providing complete context can resolve apparent disagreements.
Example: A veteran with service-connected knee problems had conflicting opinions between their VA orthopedist (who rated functional limitation as mild) and their private sports medicine specialist (who documented severe limitation). The veteran obtained an independent medical examination from a board-certified orthopedic surgeon who reviewed all imaging, treatment records, and functional tests. The independent examiner’s comprehensive report explained why the private specialist’s assessment was more accurate based on objective findings. This documentation was part of the evidence the VA reviewed when assigning a higher rating.

Mastering the Appeals Process When Requests Are Denied
When increase requests are denied, the Appeals Modernization Act provides three distinct pathways for challenging unfavorable decisions, each with specific advantages, timelines, and strategic considerations.
Veterans considering appeals can first understand how to challenge a low VA rating to determine the most effective approach for their specific situation.
Choosing the Right Decision Review Option
The three decision review options—Supplemental Claims, Higher-Level Reviews, and Board Appeals—each serve different purposes and offer unique advantages depending on specific situations, available evidence, and goals.
According to the VA, the Appeals Modernization Act provides three options when an increase request is denied: Supplemental Claim, Higher-Level Review, or Board Appeal. Each has distinct advantages and should be chosen based on specific circumstances.
Supplemental Claims work best when new and relevant evidence exists that wasn’t in the original file. This could be recent medical records, independent medical opinions, or lay statements that address the reasons for denial. Per VA guidance, a Supplemental Claim can be submitted at any time, and it preserves the original effective date if successful.
Higher-Level Reviews are appropriate when the VA may have made an error in reviewing existing evidence. A senior reviewer will look at the same evidence with fresh eyes but won’t consider new evidence. This option works well when the denial seems to have overlooked or misinterpreted evidence that was already in the file.
Board Appeals allow presenting the case to a Veterans Law Judge and can include new evidence, hearings, or both. This option takes longer but provides the most comprehensive review. This path suits complex cases or when the opportunity to present the case in person is desired.
Decision Review Options Comparison:
| Decision Review Option | Best Used When | Timeline | New Evidence Allowed |
| Supplemental Claim | New evidence is available | 4-5 months | Yes |
| Higher-Level Review | VA may have made an error | 4-5 months | No |
| Board Appeal | Complex case/hearing desired | 12-18 months | Yes (with evidence track) |

Independent Medical Evidence in VA Reviews
While veterans can pursue rating increases independently, professional medical support services provide access to experienced physicians who understand VA rating criteria and can deliver comprehensive evaluations that provide additional objective medical documentation
The Strategic Value of Professional Medical Evaluations
Professional medical evidence services connect veterans with qualified physicians who specialize in VA disability evaluations, providing thorough assessments that accurately capture condition severity using appropriate medical terminology and documentation standards that align with VA rating criteria.
Independent Medical Evaluations That Make a Difference
Working with experienced medical providers who understand VA rating criteria ensures comprehensive evaluations that capture the full scope of a condition’s impact while providing objective documentation that strengthens requests and reduces the likelihood of additional VA examination requests.
Professional medical evaluations differ significantly from routine healthcare visits. These assessments focus specifically on documenting condition severity and functional impact using VA rating criteria as the framework. The examining physician understands what the VA reviews and structures their evaluation accordingly.
These evaluations are typically more comprehensive than standard medical appointments. Detailed questioning about symptom frequency, severity, and functional limitations is followed by thorough physical or mental status examinations. Findings are documented in language that directly relates to rating criteria.
The resulting medical report provides objective, professional documentation of the condition’s current state. These reports often identify limitations or symptoms that might not be clearly documented in regular medical records, filling gaps that could otherwise affect a request.
Quality independent medical evaluations can also identify secondary conditions or complications that might warrant separate ratings, potentially increasing overall disability percentage beyond just the condition being evaluated.
Disability Benefit Questionnaires Done Right
Properly completed Disability Benefit Questionnaires from qualified physicians provide standardized medical evidence in the VA’s preferred format, presenting medical information in a standardized format and ensuring all relevant rating factors are thoroughly addressed and documented.
Disability Benefit Questionnaires (DBQs) represent the VA’s preferred format for medical evidence. When completed by qualified physicians, these standardized forms provide exactly the information VA raters need to make decisions, reducing delays and requests for additional examinations.
DBQs are condition-specific and address the exact criteria used for rating that condition. A qualified physician familiar with these forms ensures every relevant section is completed thoroughly and accurately, providing comprehensive documentation of the condition’s impact.
The standardized format makes it easier for VA raters to quickly identify the information they need. This may help VA reviewers locate relevant clinical information and may reduce the need for clarification.
Veterans interested in this approach can learn more about the VA DBQ process explained to understand how these standardized forms can strengthen their increase requests.

How REE Medical Coordinates Independent Medical Documentation
REE Medical provides veterans with access to comprehensive medical evaluations through their network of experienced medical professionals, operating within strict compliance frameworks that ensure neutrality and adherence to federal regulations while focusing exclusively on coordinating independent, objective medical documentation.
Veterans pursuing rating increases often find it challenging to obtain thorough medical evidence that accurately reflects their condition’s true impact. REE Medical connects veterans with independent medical providers who understand VA rating criteria and can conduct comprehensive evaluations focused on documenting symptom severity and functional limitations.
Their approach centers on coordinating independent, objective medical evaluations that capture the full scope of how conditions have progressed or worsened over time. The medical professionals in their network understand the specific documentation requirements for VA disability evaluations and structure their evaluations accordingly.
REE Medical operates under a strict compliance framework that ensures neutrality, transparency, and adherence to federal regulations (38 U.S.C. §§ 5901–5905). REE Medical does not prepare, present, or submit VA disability claims and does not provide legal or representational services. Their role remains limited to coordinating medical evaluations and documentation within full legal and ethical boundaries.
The company’s flat-rate pricing structure eliminates uncertainty and long-term financial commitments often associated with other services. Their nationwide network ensures veterans can access quality medical evaluations regardless of location, removing geographic barriers that might otherwise prevent access to qualified providers.
For veterans seeking updated medical documentation since their last rating or whose initial ratings didn’t adequately reflect their disability’s impact, REE Medical’s systematic approach to medical evidence development provides a access to independent medical evaluations that the VA may review.
Veterans can learn more about REE Medical’s services by visiting reemedical.com.
Final Thoughts
VA disability rating increases represent an one option available under VA regulations for veterans to receive compensation that truly reflects their service-connected conditions’ impact on their lives. The process requires understanding the system’s complexities, developing strong medical evidence, and maintaining persistence through potential challenges, but the VA evaluations determine compensation based on evidence and criteria for veterans seeking updated medical documentation.
Pursuing a VA disability rating increase isn’t just about monthly compensation—though that financial impact can be significant. It’s about ensuring the VA recognizes the true extent of how service-connected conditions affect daily life, work capacity, and overall well-being.
The process requires patience, organization, and strategic thinking. Gathering comprehensive medical evidence, understanding complex rating criteria, and potentially navigating appeals if initial requests are denied are all part of the journey. Veterans who approach this systematically, with proper preparation and strong medical documentation, put themselves in the best position for accurate evaluation.
Conditions change over time. What might have been accurately rated years ago could now warrant a higher rating due to progression, complications, or better understanding of the condition’s impact. Updated medical documentation allows the VA to assess current disability levels accurately.
Whether pursuing this independently or with professional medical support, staying informed about VA review processes is important. Effective dates are determined by VA regulations that could improve quality of life and provide the financial security veterans have earned through their service.
Disclosure
DISCLAIMER: REE Medical, LLC is not a Veterans Service Organization (VSO) or a law firm and is not affiliated with the U.S. Veterans Administration (“VA”). Results are not guaranteed, and REE Medical, LLC makes no promises. REE Medical’s staff does not provide medical advice or legal advice, and REE Medical is not a law firm. Any information discussed, such as, but not limited to, the likely chance of an increase or service connection, estimated benefit amounts, and potential new ratings, is solely based on past client generalizations and not specific to any one patient. The doctor has the right to reject and/or refuse to complete a Veteran’s Disability Benefit Questionnaire if they feel the Veteran is not being truthful. The Veteran’s Administration is the only agency that can make a determination regarding whether or not a Veteran will receive an increase in their service-connected disabilities or make a decision on whether or not a disability will be considered service-connected. This business is not sponsored by, or affiliated with, the United States Department of Veterans Affairs, any State Department of Military and Veterans Affairs, or any other federally chartered veterans service organization.